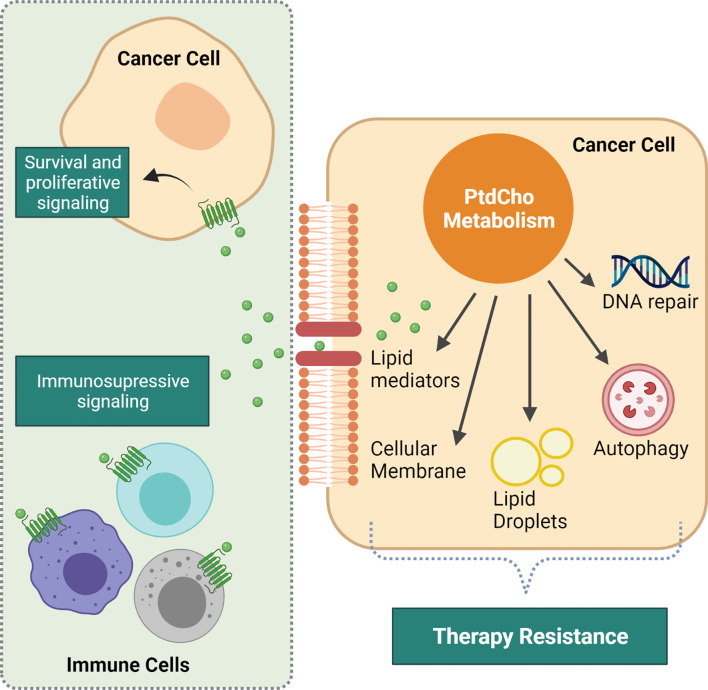
Figure 1.
Intracellular and intercellular consequences of altered phosphatidylcholine (PtdCho) metabolism that impacts response to therapy. Increased PtdCho metabolism supports cancer cell accelerated growth by providing the major cellular membrane component. Additionally, PtdCho promotes intracellular events that mediate resistance to therapy, such as DNA repair, lipid droplet synthesis, and autophagy process. PtdCho-derived lipid mediators are prominent drivers of resistance. They are recognized by their cognate receptors present both in cancer cells and immune microenvironment cells, driving cancer cell survival and proliferation and promoting immunosuppression. Created with BioRender.com.