FIG. 7.
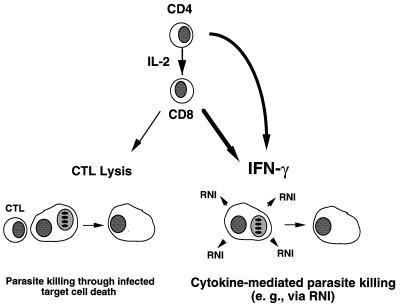
Dual role of CD8+ T lymphocytes as effectors of immunity to T. gondii. Priming of resting CD8+ cells, which requires parasite Ag, CD4+ T cells, and IL-2, results in anti-parasite effectors. These cells display MHC class I-restricted cytolytic activity toward Toxoplasma-infected target cells and release high levels of IFN-γ in response to parasite stimulation. Based upon studies in IFN-γ and perforin KO mouse strains, cytokine secretion is the major effector activity of CD8+ cells in acute and vaccine models of infection. IFN-γ acts, at least in part, through its ability to induce macrophage microbicidal functions such as NO production. Nevertheless, CTL function appears to play a secondary functional role in protection during chronic infection, as measured by increased mortality and incidence of brain cysts in perforin KO animals.