Figure 3.
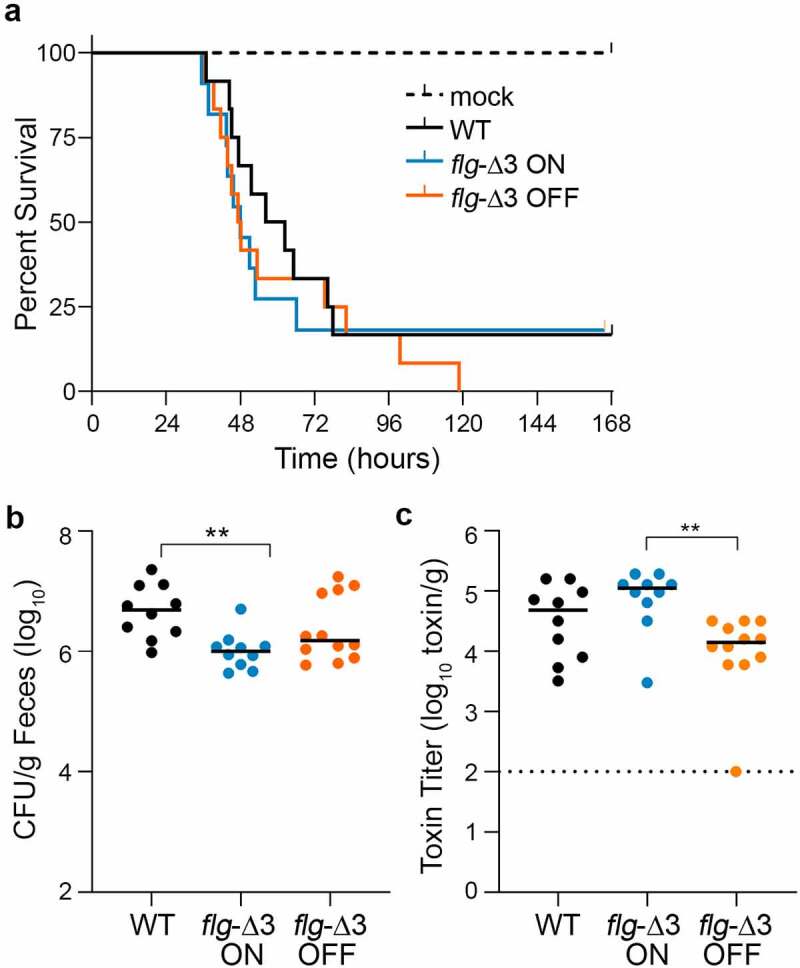
Interfering with flagellar switch inversion affects toxin accumulation and bacterial burden in a hamster model of CDI. Antibiotic-treated male and female Syrian Golden hamsters were inoculated with 1,000 spores of wildtype R20291 (WT), flg-Δ3 ON, and flg-Δ3 OFF. Mock-inoculated animals were included in each experiment. Data are combined from two independent experiments testing strains in 3 male and 3 female hamsters, for 12 total hamsters per strain. (a) Kaplan–Meier analysis of survival. (b) CFU in cecal contents. **p < 0.01 by Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn’s posttest. (c) Toxin titers in cecal contents calculated as the reciprocal of the highest dilution to cause ≥80% rounding of Vero cells. No cell rounding occurred when treated with diluted cecal contents from mock-inoculated animals. Bars indicate the means; dotted line represents the limit of detection. **p < 0.01 with Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn’s posttest. (b, c, d) Symbols indicate CFU from individual animals and bars indicate medians.
