Figure 2.
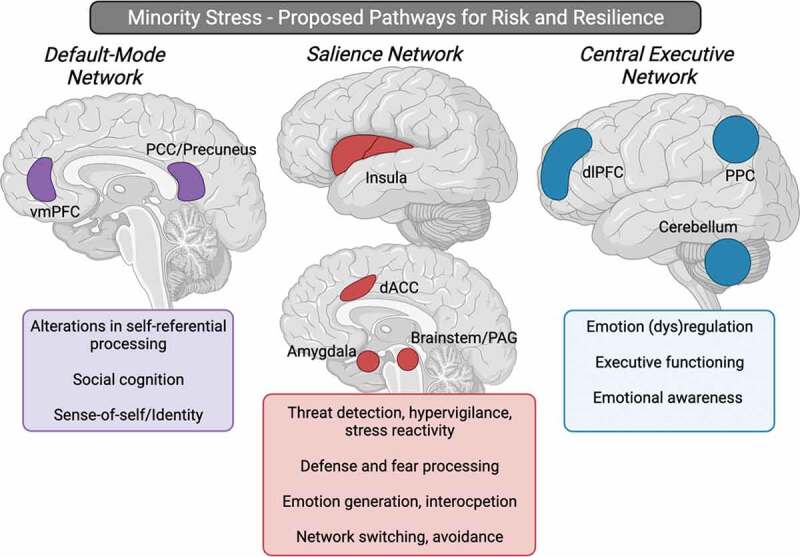
Proposed minority stress neural network pathways that may be associated with risk and resilience for psychopathology. The default-mode network, with key hubs within the vmPFC, and PCC/precuneus, may be associated with alterations in self-referential processing, social cognition, and sense-of-self/identity following minority stress exposure. The salience network, involving the insula, dACC, amygdala, and brainstem, may display altered functioning following minority stress exposure, subserving changes in threat detection, hypervigilance, and stress reactivity, as well as defence and fear processing, emotion generation, interoception, and avoidance. The central executive network, with key hubs involving the dlPFC, PPC, and the cerebellum may be involved in alterations observed in emotion regulation, executive functioning, and emotional awareness following minority stress exposure. Taken together, these alterations within intrinsic connectivity networks in the brain may be associated with the disproportionally higher rates of transdiagnostic psychopathology observed among sexual minorities (such as increased PTSD, depression, anxiety, suicidality, and substance use). Abbreviations; vmPFC = ventromedial prefrontal cortex, PCC = posterior cingulate cortex, dACC = dorsal anterior cingulate cortex, PAG = periaqueductal grey, dlPFC = dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, PPC = posterior parietal cortex. Figure created with BioRender.com.
