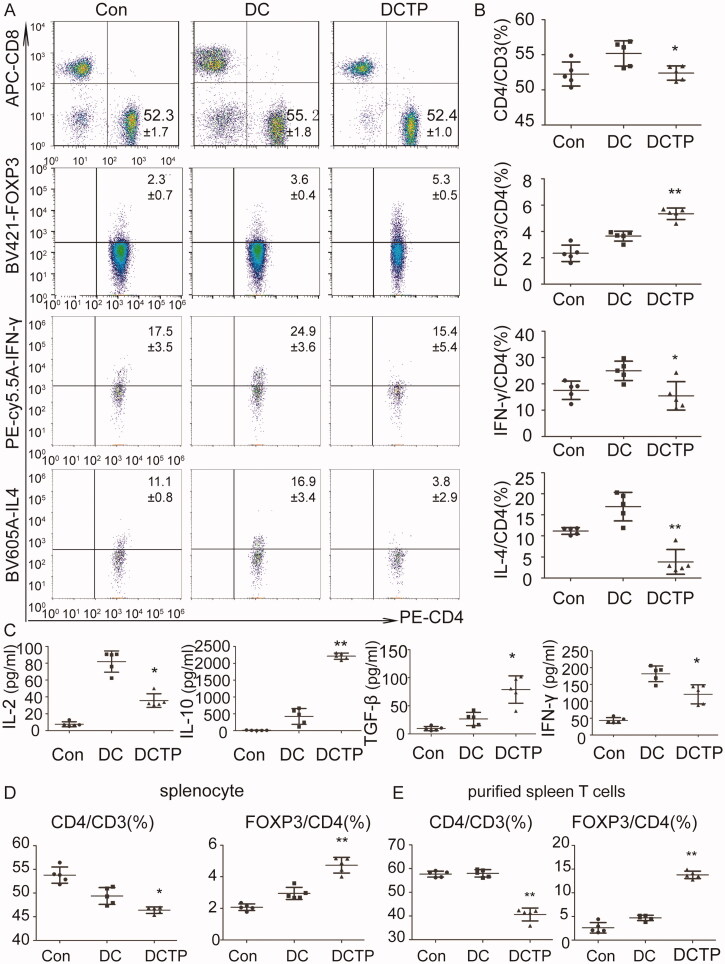
Figure 7.
Tolerogenic DCs elicited T cell-dependent immunosuppression. Splenocytes or lymph node cells were isolated and cocultured with DCs or DCTP for 72 hours. Then, T cells and cytokines were analyzed. (A, B) FCM analysis of CD3+CD4+ T cells, CD3+CD4+FOXP3+ Tregs, CD3+CD4+IFN-γ+ Th1 cells, and CD3+CD4+IL4+ Th2 cells isolated from the lymph nodes. A significant decrease in the number of CD4+ T lymphocytes and an increase in Tregs were detected in DCTP cocultures compared with DC cocultures. IL4- and IFN-γ-positive T cells both showed significant reductions (numbers represent mean ± SD). (C) Measurement of IL-2, IL-10, IFN-γ, and TGF-β levels in supernatants from lymph node cells cocultured with DCs or DCTP by ELISA. (D) FCM analysis of CD3+CD4+ T cells and CD3+CD4+FOXP3+ Tregs isolated from the spleen. (E) T cells were purified from the spleen and cocultured with DCs or DCTP. FCM analysis of CD4+ T cells and Tregs showed more obvious changes consistent with those observed with mixed splenocytes. Experiments were repeated three times in quintuplicate each time (n = 15) (two-tailed t-test, *p<.05, **p<.01).