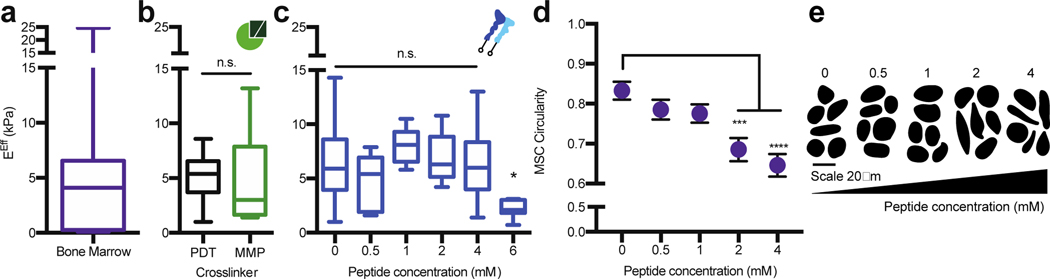
Figure 4. The PEG hydrogel accurately models the bulk compressive properties of bone marrow tissue.
a) Rheology data from Jansen et al., 20151 for the effective Young’s modulus (EEff) of porcine bone marrow at 35°C. b) The EEff for 20 wt%, 8-arm, 20K PEG hydrogels crosslinked at a 1:1 thiol to maleimide molar ratio with 1.5 kDa PEG-dithiol (PDT, black) or with the bone marrow cocktail containing MMP crosslinkers (MMP, green). c) The EEff for 20 wt%, 8-arm, 20K PEG hydrogels crosslinked at a 1:1 thiol to maleimide molar ratio with PDT and coupled with different concentrations of the bone marrow peptide cocktail for 10 minutes before gelation. d) MSCs circularity with respect to peptide concentration and e) representative cell traces for cells encapsulated in a 20 wt%, 8-arm, 20 kDa PEG-crosslinked with the bone marrow cocktail. The significance is determined using a two-tailed t-test where p=0.05, and error bars represent the SEM. (N≥2, n≥3 for mechanical testing; N≥2, n≥10 for cell circularity).