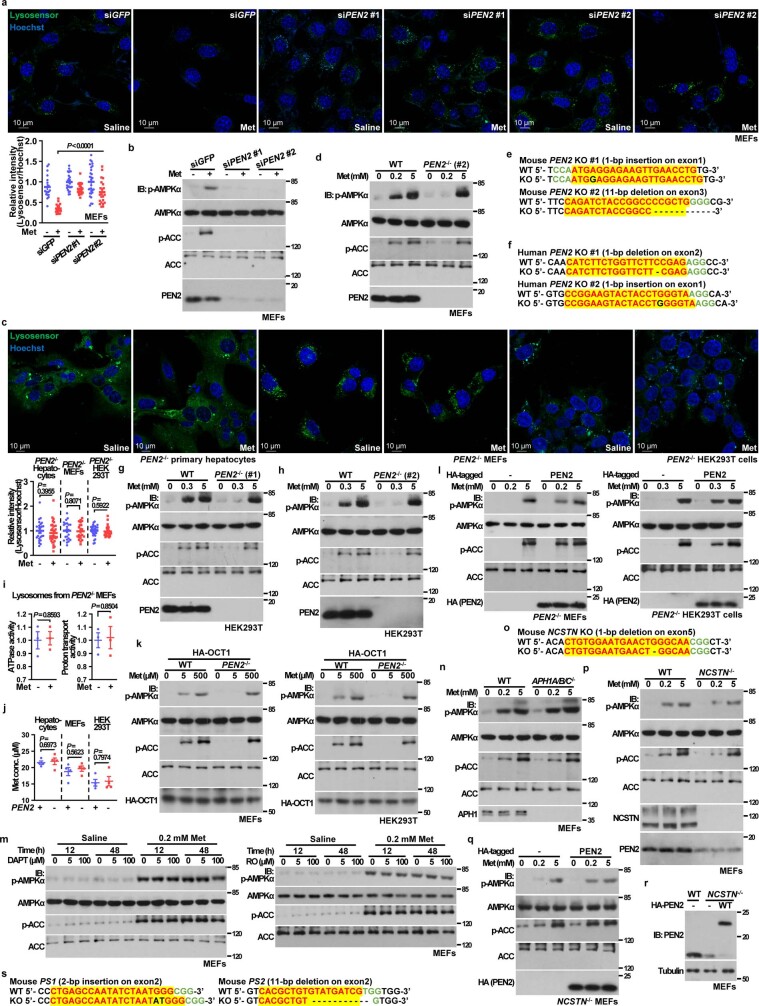
Extended Data Fig. 3. PEN2 is required for AMPK activation by low metformin.
a, b, Knockdown of PEN2 impairs the activation of AMPK, and inhibition of v-ATPase by metformin. MEFs infected with lentivirus carrying two distinct siRNAs (#1 or 2#) against PEN2, or GFP as a control, were treated with 200 μM metformin for 12 h, representative images of the experiments shown in a upper, followed by analysis of the lysosomal pH [a lower, shown as mean ± s.e.m., n = 20 (control) and 21 (metformin-treated) cells for siGFP, n = 25 cells for siPEN2#1, and n = 29 (control) and 22 (metformin-treated) cells for siPEN2#2, all from 2 dishes/experiments; and P value by two-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey] and the determination of p-AMPKα and p-ACC (b). c, Knockout of PEN2 abrogates the inhibition of v-ATPase by metformin in mouse primary hepatocytes (left panel), MEFs (middle panel), and HEK293T cells (right panel). MEFs, HEK293T cells were treated with 200, 300 μM metformin for 12 h, mouse primary hepatocytes were treated with 5 μM metformin for 2 h, and then labelled with Lysosensor, along with Hoechst. The lysosomal pH was determined as in Fig. 1a. Data are shown as mean ± s.e.m., n = 26 (control) and 31 (metformin-treated) from 6 dishes/experiments for primary hepatocytes, n = 25 (control) and 22 (metformin-treated) from 4 dishes/experiments for MEFs, and n = 30 (control) and 29 (metformin-treated) from 6 dishes/experiments for HEK293T cells; P value within each cell type was determined by two-sided Student’s t-test. d, g, h, k, Knockout of PEN2 blocks AMPK activation by low metformin. Clone #2 of PEN2-/- MEFs (d) treated with 200 μM (low concentration) metformin, or clone #1 and clone #2 of PEN2-/- HEK293T cells (g and h), treated with 300 μM (low concentration for the cell line) metformin, or OCT1-expressing PEN2-/- MEFs and HEK293T cells treated with 5 μM (low concentration) metformin (k) or 5 mM (high concentration, as a control for d, g and h), 500 μM metformin (high concentration, for k), for 12 h (d, g and h) or 2 h (k), were subjected to immunoblotting for the analysis of p-AMPKα and p-ACC. See also results with clone #1 of PEN2-/- MEFs in Fig. 2c. e, f, Strategies to generate MEFs (e) and HEK293T cells (f) with knockout of PEN2. Two distinct sets of sgRNAs for each cell line, whose sequences are listed in Methods section, were applied to generate PEN2-/- cells. Two clones (#1 and #2) for each cell line type were established. i, Knockout of PEN2 blocks the inhibition of v-ATPase by metformin in purified lysosomes. Lysosomes purified from PEN2-/- MEFs were incubated with 5 μM metformin for 1 h. The activity of v-ATPase was determined as in Extended Data Fig. 1d. Data are shown as mean ± s.e.m.; n = 3 for each condition, and P value by two-sided Student’s t-test. j, Knockout of PEN2 does not affect metformin uptake. Mouse primary hepatocytes, MEFs and HEK293T cells were treated as in c, followed by determining intracellular metformin concentrations. Data are shown as mean ± s.e.m., n = 4 for each genotype, and P value within each cell type by two-sided Student’s t-test. l, Re-introduction of PEN2 into PEN2-/- MEFs or HEK293T cells restores AMPK activation. PEN2-/- MEFs (left panel) or HEK293T cells (right panel) were infected with lentiviruses expressing HA-tagged PEN2 (all expressed at close-to-endogenous levels driven by pBOBI vector). Cells were treated with 200 or 300 μM (low concentration), or 5 mM (high concentration, as a control) metformin for 12 h, followed by analysis of p-AMPKα and p-ACC. m, Activity of the γ-secretase holoenzyme is dispensable for metformin-induced AMPK activation. MEFs were treated with DAPT (left panel) or RO4929097 (RO, right panel) at indicated concentrations for 12 h or 48 h. Twelve hours before lysis, cells were treated with 200 μM metformin, then lysed for analysis of p-AMPKα and p-ACC. n, Loss of APH1 does not affect metformin-induced activation of AMPK. MEFs with APH1A, APH1B and APH1C triple knockout were treated with 200 μM or 5 mM metformin for 12 h, followed by analysis of p-AMPKα and p-ACC. o, Strategies to generate MEFs with knockout of nicastrin. sgRNAs against NCSTN, whose sequences are listed in Methods section, were applied to generate NCSTN-/- MEFs. p, q, Knockout of NCSTN, through decreasing the protein levels of PEN2, impairs metformin-induced activation of AMPK. NCSTN-/- MEFs (p) or NCSTN-/- MEFs with HA-tagged PEN2 expressed (q, expressed at close-to-endogenous levels driven by the lentiviral system using pBOBI vector, as validated in r) were treated with 200 μM (low concentration) or 5 mM (high concentration, as a control) metformin for 12 h, followed by analysis of p-AMPKα and p-ACC. r, Protein levels of PEN2 in MEFs with knockout of NCSTN. Cells were lysed for analysis of PEN2 protein levels by immunoblotting, followed by densitometry analysis. s, Strategies to generate MEFs with knockout of presenilins. sgRNAs against PS1 (left panel) and PS2 (right panel), whose sequences are listed in Methods section, were applied to generate PS1- or PS2-KO MEFs. Experiments in this figure were performed three times, except b, h, l, four times.