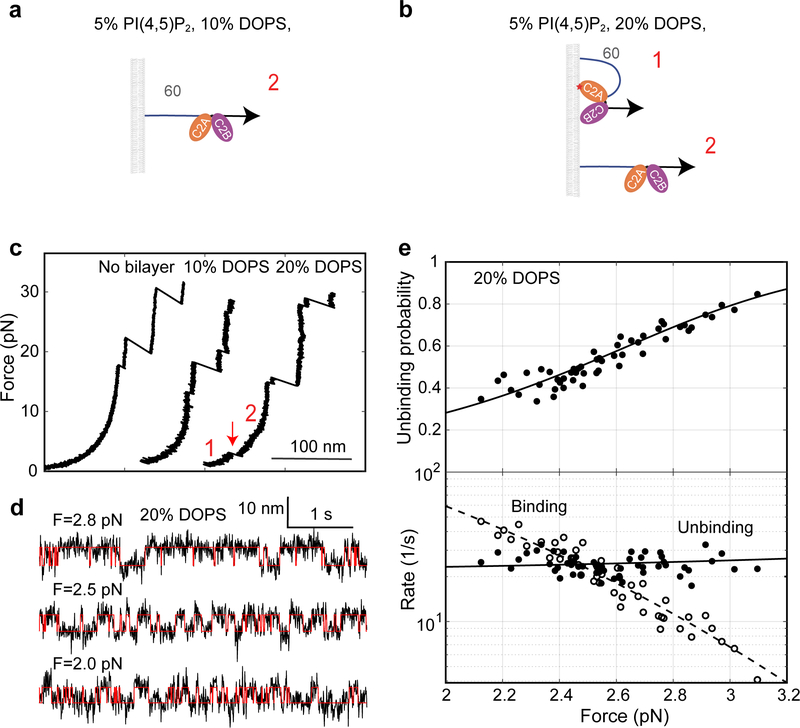
Extended Data Fig. 4. E-Syt1 C2AB only weakly binds to membranes enriched with negatively charged lipids.
(a, b) Diagrams showing no binding (a) and weak binding (b) of the E-Syt1 C2AB domain in the presence of 10% and 20% DOPS, respectively. (c) Force-extension curves showing no membrane binding of E-Syt1 C2AB domain in the absence of supported bilayer or in the presence of the supported bilayer containing 10% DOPS. Weak binding was detected in the presence of 20% DOPS, as indicated by the rip at low force (red arrow). (d) Extension-time trajectories at constant forces (black curves) and their idealized transitions derived from hidden-Markov modeling (red curves). (e) Unbinding probability and binding and unbinding rates (symbols) and their best model fits (lines). The fitting revealed an unbinding energy of 4.4 (±0.3) kBT for the E-Syt1 C2AB domain (Supplementary Table 2).