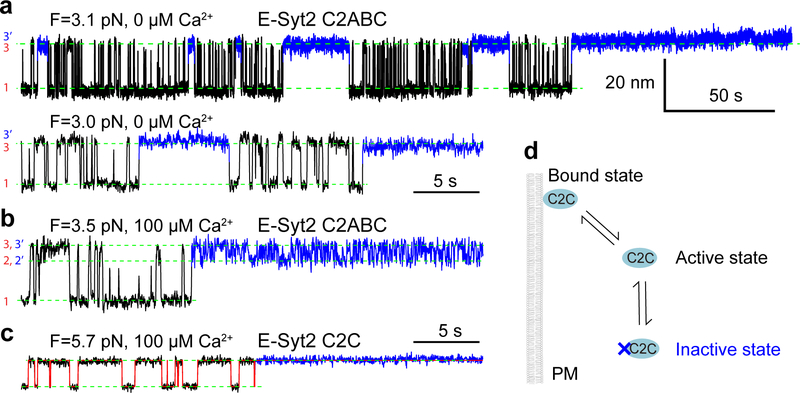
Extended Data Fig. 7. E-Syt2 C2C undergoes a reversible force-dependent, but Ca2+-independent conformational change to inactivate its membrane binding.
(a-c) Extension-time trajectories at constant force in the absence (a) and presence (b) of Ca2+ for E-Syt2 C2ABC or in the presence of Ca2+ for E-Syt2 C2C (c). The long gaps in the unbound state highlighted blue represent the binding inactive state. (d) Diagram of the conformational transition of the C2 domain in the binding active and inactive states.