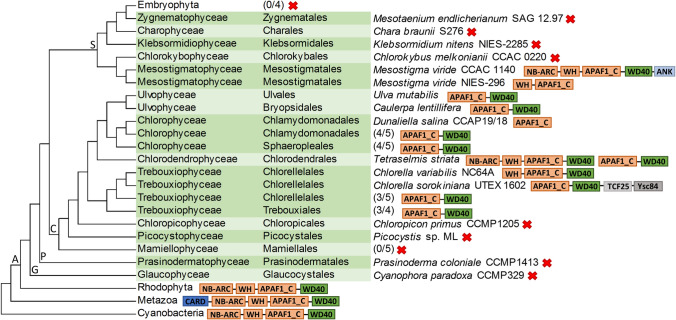
Fig. 3.
Cladogram showing the domain architectures of the retrieved APAF1_C/WD40 domain-encoding genes and the phylogenetic relationship of the lineages in which they were identified. The relationship among Archaeplastida lineages (A) follows Li et al. (2020). The position of Picocystophyceae basal to Chloropicophyceae is according to Turmel et al. (2019). For Streptophyta (S) (except Embryophytes), Chlorophyta (C), Prasinodermaphyta (P) and Glaucophyta (G), the taxonomic class and order of the studied species are according to AlgaeBase (Guiry and Guiry 2021). The nomenclature of C. melkonianii follows the recent revision of the Chlorokyboceae by Irisarri et al. (2021). Numbers in brackets are fractions of the total number of species (some species include multiple accessions, see Supplementary Table S2) in which the depicted APAF1_C/WD40 module was positively identified, whereas red crosses indicate that no homologs were identified in the corresponding lineage. Protein domain abbreviations: ANK (Ankyrin repeat-containing domain), APAF1_C (apoptotic protease activating factor 1 helical domain), CARD (caspase activation and recruitment domain), NB-ARC (nucleotide-binding adaptor shared by APAF1, certain R-gene products and CED-4), TCF25 (transcription factor 25), WD40 (WD40 domain-containing repeat), WH (winged helix-like DNA-binding domain superfamily). Protein domain lengths are not to scale