Fig. 5.
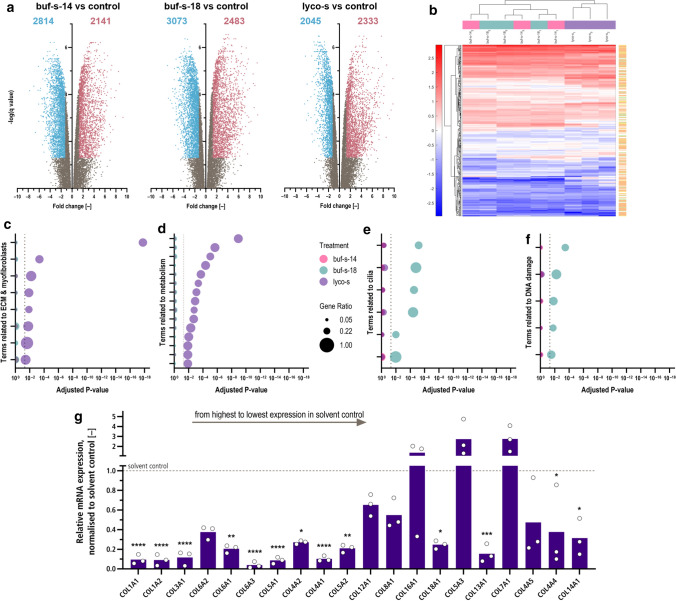
mRNA expression analysis of HCF reveals repression of ECM and collagen function after treatment with lyco-s. a Out of 61,043 transcripts, 18,964 remained after exclusion of low-expressed transcripts. Volcano plots show over 4000 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) for all three treatments. Treatment with lyco-s led to a similar amount of significantly up- (red), but not down-regulated genes (blue) compared to bufalin similars. n = 3 biological replicates (donors). Discoveries (Q = 0.05) adjusted following BY. b Treatment with lyco-s leads to increased deregulation of central pathways related to ECM function, including ECM organisation (orange), collagen binding (green), or both (yellow). GO:BP analysis of DEGs highlights downregulation of ECM and myofibroblast functions (c) as well as metabolism (d) after treatment with lyco-s. In contrast, treatment with buf-s-18 led to downregulation of genes involved in cilia (e) and DNA damage responses (f). For samples treated with buf-s-14, no terms were significantly enriched after multiplicity adjustment. Dotted line indicates significance threshold (padj. < 0.05). g Treatment with lyco-s (purple) repressed most high to medium-expressed collagen isoforms in HCF. The top 5 collagens are among the top 20 overall genes (compare Supplementary Fig. 4d). Mean (bars) and single biological replicates (circles), asterisk indicates significance in Two-way ANOVA (p < 0.05), adjusted following Dunnett (including buf-s-14 + buf-s-18, see Supplementary Fig. 4d)