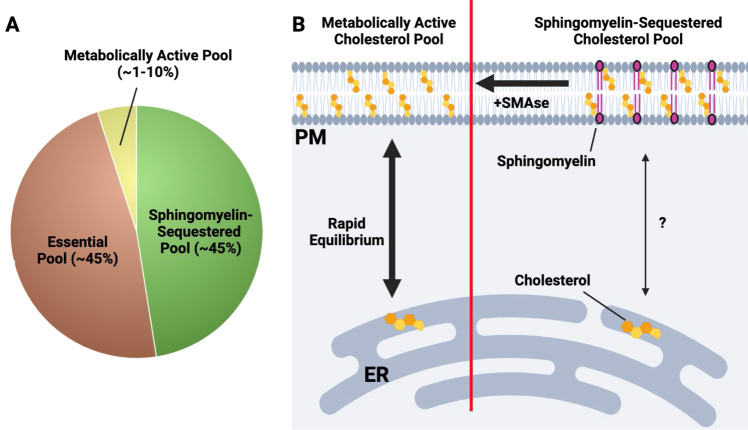
Fig. 2. An overview of the three-cholesterol pool model in the plasma membrane.
A The plasma membrane (PM) contains at least three distinct pools of cholesterol. The metabolically active or accessible cholesterol pool makes up ~1–10% of total PM cholesterol. Sphingomyelin-sequestered cholesterol and the essential pool are each estimated to be ~45% of total PM cholesterol. B Depiction of the metabolically active and sphingomyelin-sequestered cholesterol pools. On the left side of the diagram, the metabolically active cholesterol pool rapidly equilibrates with the ER cholesterol pool, thereby providing a metabolic conduit for ER-resident cholesterol sensing machinery (e.g., SCAP-SREBP, HMGCR) to sense PM cholesterol levels. On the right, the sphingomyelin-sequestered cholesterol pool is composed of cholesterol molecules that are tightly associated with sphingomyelin and likely other phospholipid species. In contrast with the metabolically active cholesterol pool, the SM-associated cholesterol pool does not rapidly equilibrate with the ER cholesterol pool. Treatment of cells with bacterial sphingomyelinase (SMase) liberates SM-associated cholesterol, allowing it to enter the metabolically active pool. The essential pool (not shown) is less well understood and thought to play a fundamental role in the bilayer integrity of the plasma membrane