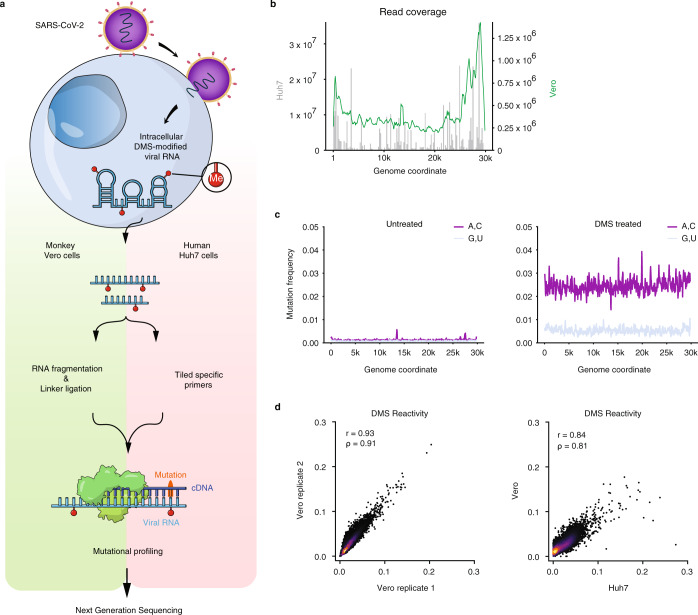
Fig. 1. Genome-wide probing of SARS-CoV-2 RNA structure in infected Vero and Huh7 cells with DMS-MaPseq.
a Schematic of the experimental protocol for probing severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) RNA structures in Vero and Huh7 cells using dimethyl sulfate mutational profiling with sequencing (DMS-MaPseq). b Read coverage as a function of genome coordinate for Huh7 cells using tiling specific primers (gray bars, left axis) and Vero cells using linker ligation (green curve, right axis); Vero coverage was smoothed by taking the mean over a sliding window of 500 nt. c Signal vs. noise plots of mutation frequencies (i.e., among all reads aligning to each genome coordinate, the fraction of reads with a mutation at that coordinate) on adenines (As) and cytosines (Cs) vs. guanines (Gs) and uracils (Us) as a function of genome coordinate for untreated and DMS-treated RNA. A mutation frequency of 0.01 at a given position represents 1% of reads having a mismatch or deletion at that position. Signal and noise were smoothed by taking the mean over 100 nt windows in increments of 50 nt. d Comparison of DMS reactivities on As and Cs between biological replicates in Vero cells (left) and between the averaged of Vero replicates and Huh7 cells (right). Pearson (r) and Spearman (ρ) correlation coefficients are shown. For each sample, the top 0.05% of mutational fractions (values over 0.27 for Vero and 0.38 for Huh7) were considered outliers and excluded from the plot and calculation of correlation coefficients. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.