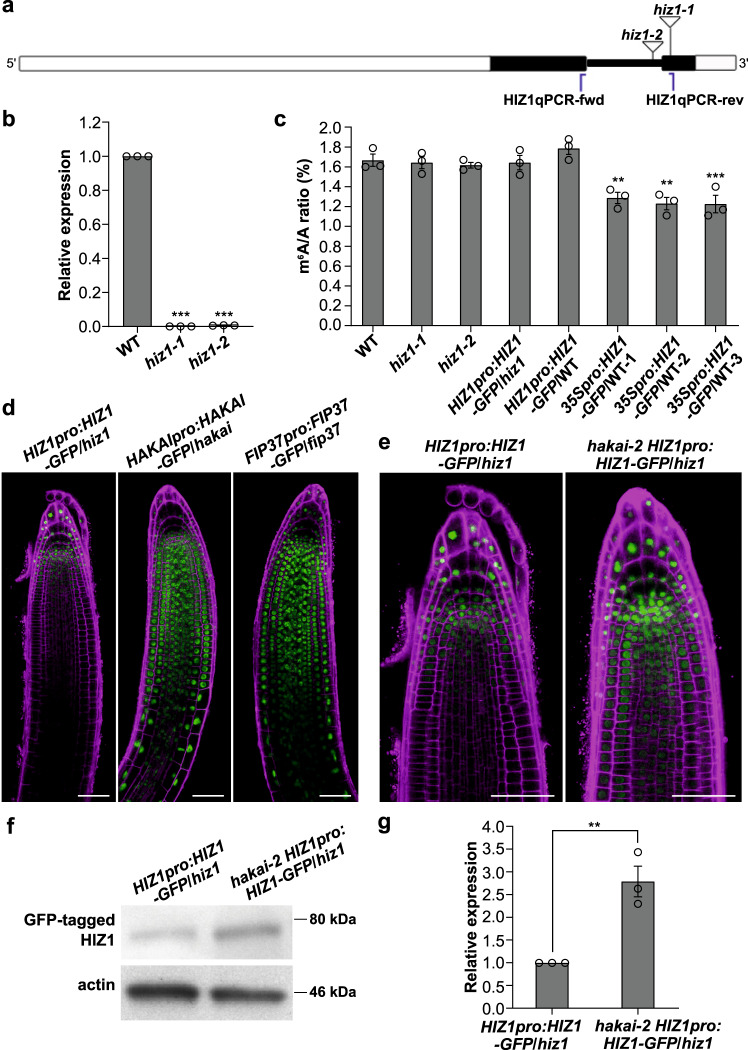
Fig. 2. Characterizing Arabidopsis HIZ1.
a Schematic of HIZ1 (AT1G32360) genomic DNA sequence with T-DNA insertion sites and the primer pair used for RT-qPCR. White rectangles denote UTRs of HIZ1 genomic DNA, black rectangles denote exons and thick black lines represent introns. hiz1-1 refers to Salk_045882 and hiz1-2 refers to Salk_000717. Blue lines represent the locations of primers. b The transcript levels of HIZ1 analyzed by RT-qPCR using the primer pair labeled in a. CBP20 was used as a reference gene. Data here and in c represent mean ± SE from three biological replicates and statistically significant differences relative to WT were analyzed by One-Way ANOVA (one-sided test) and marked with asterisks (**p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001). p < 0.0001 (hiz1-1); p < 0.0001 (hiz1-2). c m6A levels checked by two-dimensional thin layer chromatography (TLC) analysis. In one-way ANOVA test, p = 0.9996 (hiz1-1); p = 0.9907 (hiz1-2); p = 0.9996 (HIZ1pro:HIZ1-GFP/hiz1); p = 0.6393 (HIZ1pro:HIZ1-GFP/WT); p = 0.0036 (35Spro:HIZ1-GFP/WT-1); p = 0.001 (35Spro:HIZ1-GFP/WT-2); p = 0.0009 (35Spro:HIZ1-GFP/WT-3). d, e Localization of GFP-tagged proteins in primary root tips of 3-day-old seedlings. Scale bar = 50 μm. Experiments in d, e were repeated independently at least three times, and representative images are shown. f Western blot demonstrating the increased protein level of GFP-tagged HIZ1 in the hakai-2 background. Experiments in f were repeated independently three times with similar results. g Transcript levels of HIZ1pro:HIZ1-GFP analyzed by RT-qPCR using the same primer pair as that in b. CBP20 was used as a reference gene. Data represent mean ± SE from three biological replicates and the statistically significant difference was analyzed by two-sided unpaired t-test and marked with asterisks (**p < 0.01). p = 0.0061. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.