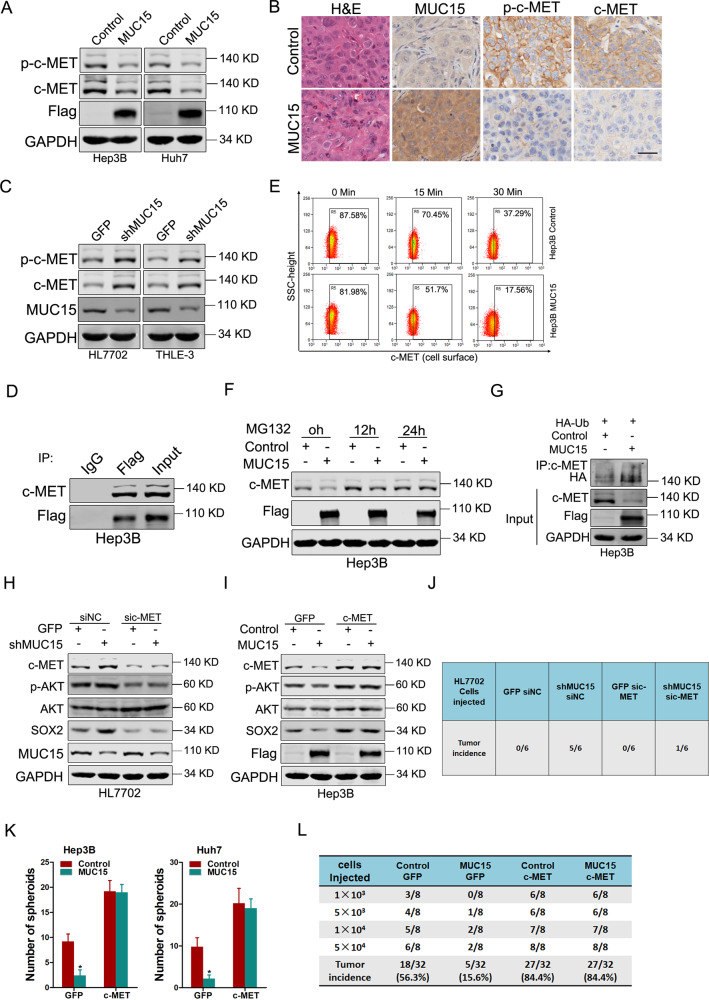
Fig. 4. MUC15 modulates c-MET/PI3K/AKT/SOX2 signaling in liver T-ICs.
A Phosphorylation of c-MET and total c-MET in Hep3B/Huh7 MUC15 and control spheroids was determined by western blot. B Immunohistochemical staining of p-c-MET and c-MET in xenografted tumors generated by Hep3B MUC15 and control spheroid. Scale bar = 25 μm. C The expression of p-c-MET and c-MET in shMUC15 and control hepatocyte cells was determined by western blot. D Endogenous c-MET and Flag-tagged MUC15 were immunoprecipitated. E The cell surface expression levels of c-MET in Hep3B MUC15 and control spheroids were determined using flow cytometry. F Hep3B MUC15 and control spheroids were treated with MG132 (20 μM) for indicated times and then subjected to western-blot analysis. G Hep3B MUC15 and control spheroids were transfected with hemagglutinin (HA)-tagged ubiquitin and then total ubiquitinated proteins were detected by Western blotting for HA. H HL7702 shMUC15 and control cells transfected with sic-MET or siNC were subjected to western blot analysis. I Hep3B MUC15 and control cells infected with c-MET overexpression virus were subjected to western blot analysis. J HL7702 shMUC15 and control cells were transfected with sic-MET or siNC and were then injected subcutaneously into NOD-SCID mice at 1 × 103 cells per mouse. Xenografted tumor formation was monitored 10 weeks later. K Hep3B/Huh7 MUC15 and control cells were infected with c-MET overexpression virus and were then subjected to spheroids formation assay. L In vivo limiting dilution assay of indicated HCC cells. Tumors were observed over 2 months; n = 8 for each group. All results are presented as the mean ± SD, and statistical significance was assessed using a two-tailed Student t-test. *p < 0.05.