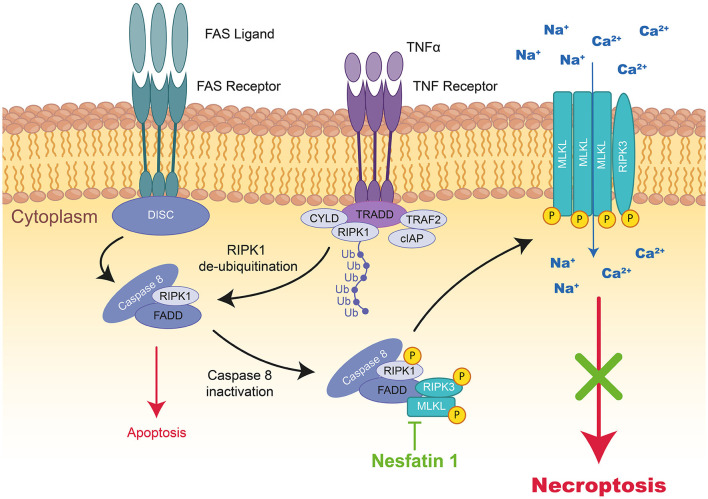
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of necroptosis and the mode of action of Nesfatin 1 therapeutic peptide during MIRI. TNFα activates the TNF receptor, which induces the formation of a complex formed by TRADD, TRAF2, RIPK1, CYLD, and cIAP1 at the cytoplasmic membrane. In the absence of cIAP1, RIPK1, FADD, and Caspase-8 form cytosolic DICS complex, Caspase-dependent pathways are activated inducing apoptosis. However, by Caspase-8 inactivation, RIPK1 interacts with RIPk3 and MLKL to form a third complex inducing necroptosis. The kinase of RIPK1 phosphorylates RIPK3 and MLKL resulting in their translocation to the plasma membrane, where the complex mediates membrane permeabilization. The therapeutic peptide Nesfatin-1 (highlighted in green) can reduce RIPK1, RIPK3, and MLKL expression and therefore necroptosis. TNF, tumor necrosis factor; TRADD, tumor necrosis factor receptor type 1-associated death domain; TRAF2, TNF receptor-associated factor 2; RIPK1/3, receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 1; CYLD, lysine 63 deubiquitinase; cIAP1, cellular inhibitor of apoptosis protein 1; MLKL, mixed lineage kinase domain like pseudo kinase.