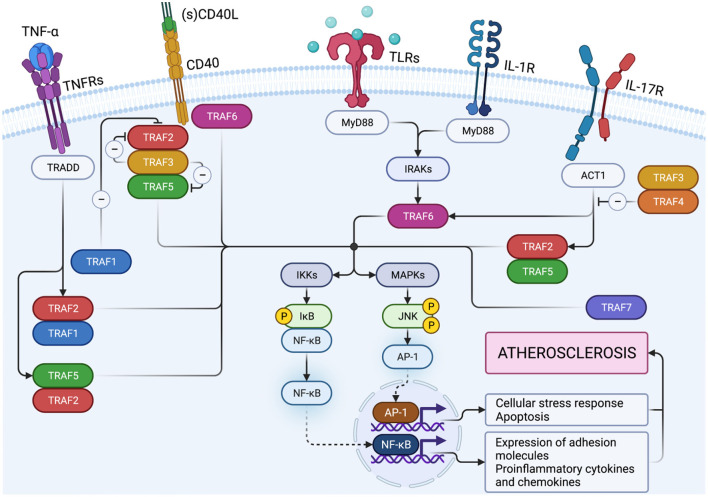
Figure 2.
TNF-receptor associated factors (TRAFs) link proximal receptor ligation and distal signaling pathways. Upon TNF-binding, TNFR1 activates inflammatory signaling pathways via TRAF1, TRAF2, and TRAF5. CD40 ligation induces canonical and non-canonical NF-κB activation by TRAF2/5 and canonical NF-κB activation by TRAF6. TRAF3 inhibits NF-κB activation mediated by TRAF2/5 but does not interfere with transcriptional activity of TRAF6-mediated NF-κB. TRAF1 inactivates TRAF2 by direct binding and is considered an inhibitory TRAF. Activation of TLRs and IL-1R can promote MyD88 dependent TRAF6 activity. Following binding of IL-17, heteromeric IL-17RA and IL-17RC recruit TRAF2, TRAF5, and TRAF6 via the adaptor protein Act1 to induce activation of downstream signaling pathways. TRAF3 and TRAF4 on the other hand, inhibit IL-17 signaling by interaction with IL-17R or Act1, respectively. Created with BioRender.com.