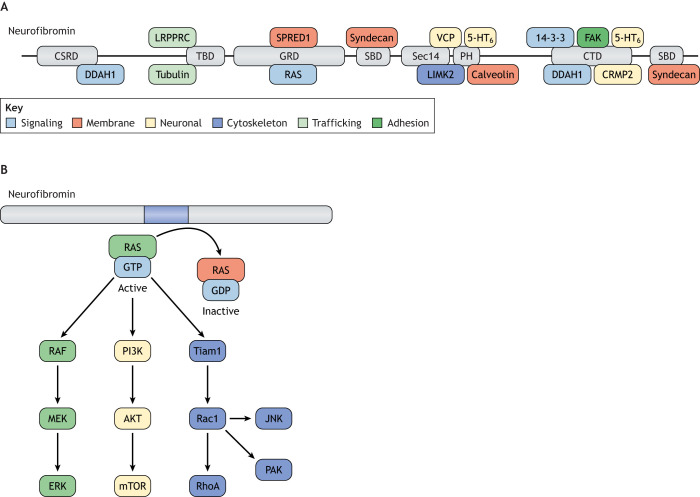
Fig. 2.
Neurofibromin binding partners and canonical RAS signaling. (A) Neurofibromin is a large molecule, containing numerous predicted protein domains, which have been shown to interact with a diverse set of binding partners. Protein domains are as follows: cysteine-serine rich domain (CSRD), GAP-related domain (GRD), C-terminal domain (CTD), pleckstrin homology domain (PH), syndecan-binding domain (SBD), Sec-14 domain (Sec14), tubulin-binding domain (TBD). The position of domains with which the interacting proteins bind is shown. Neurofibromin binding partners are categorized by function in the key. Adapted from Ratner and Miller (2015). This image is not published under the terms of the CC-BY license of this article. For permission to reuse, please see Ratner and Miller (2015). (B) The neurofibromin GRD functions to accelerate the conversion of active GTP-bound RAS to its inactive GDP-bound form. Active RAS can activate numerous distinct downstream effectors to result in increased RAF/MEK.