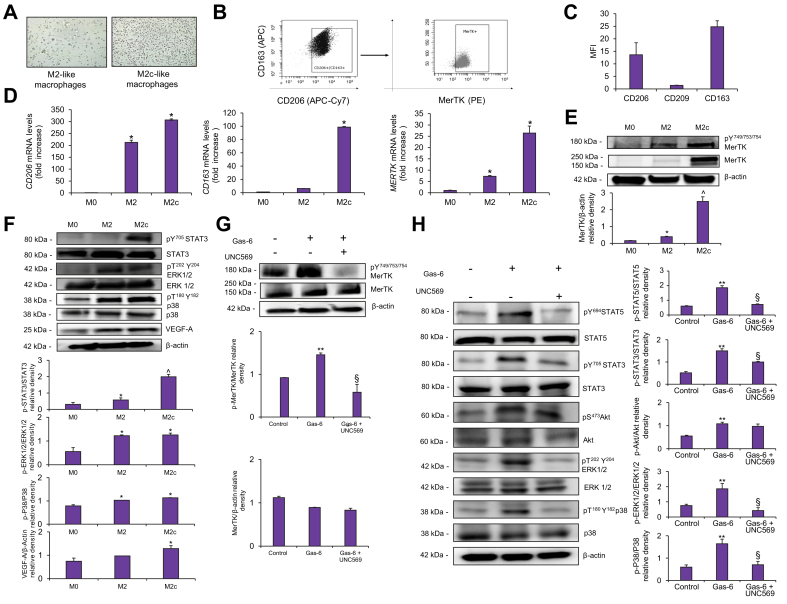
Fig. 5.
Expression and activation of MerTK and downstream signaling in monocytes differentiated towards M2c-like macrophages.
(A) Morphologic analysis of culture of naïve (M0) macrophages derived from peripheral blood monocytes and of peripheral blood monocytes that were treated with M-CSF (50 ng/ml) for 5 days (M2-like macrophages), followed by cultivation with M-CSF (50 ng/ml) and IL-10 (50 ng/ml) for additional 3 days (M2c-like macrophages). (B-C) Cells were stained for CD206, CD163, CD209 or MerTK and analyzed by flow cytometry. (B) Representative Dot plots depicting the gating strategy for analyzing MerTK expression in (CD206+ CD163+ CD209-) macrophages. (C) Histograms show MFI. (D) CD206 CD163 and MERTK mRNA expression was analyzed by qRT-PCR and normalized to β-actin. (E-F) Macrophages were deprived of serum and lysed. (G-H) Serum-deprived M2c macrophages were exposed to UNC569 or DMSO for 90 min before stimulation with Gas-6 for 15 min. 30 μg of cell lysates were analyzed by western blotting to detect different proteins or phosphoproteins. Densitometries of MerTK/ β-Actin, p-MerTK/MerTK, p-STAT3/STAT3, p-STAT5/STAT5, p-Akt/Akt p-ERK1/2/ERK1/2, p-P38/P38 and VEGF-A/ β-Actin expression (n = 3) were shown in the graphs. Data are mean ± SEM. Statistical significance was assessed by Student's t test. ∗p <0.05 vs. M0 macrophages; ˆp <0.05 vs. M2 macrophages; ∗∗p <0.05 vs. Control M2c; §p <0.05 vs. M2c macrophage stimulated with Gas-6 without inhibition for MerTK. M-CSF, macrophage colony-stimulating factor; MFI, mean fluorescence intensity; qRT-PCR, quantitative real-time PCR.