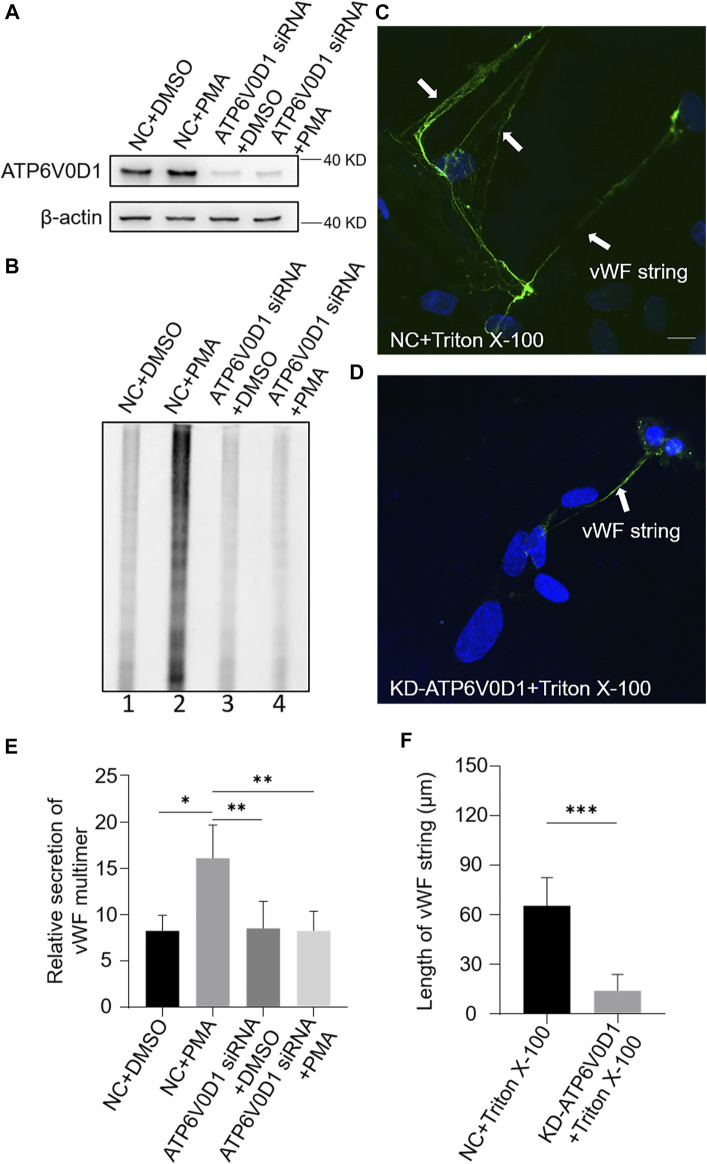
FIGURE 7.
vWF secretion and the ability to generate surface strings are also compromised in KD-ATP6V0D1 human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Negative control (NC) and ATP6V0D1 siRNA were transfected into two groups of HUVECs, respectively. At 72 h later, one group of NC and KD-ATP6V0D1 cells was exposed to 80 nM PMA for 30 min to stimulate Weibel–Palade body secretion, and the other groups were exposed to DMSO (0.1%) instead. (A) Western blotting analysis of the detection of ATP6V0D1 knockdown in cell lysate collection. (B, E) Western blotting analysis of the detection of vWF multimer secretion in supernatant. Multimer gels were analyzed using the NIH ImageJ software. The quantification of supernatant vWF multimers was carried out based on the normalization of the β-actin protein level of the cells in each well. n = 5, *p < 0.05,**p < 0.01. (C, D) 1% Triton X-100 was added into the culture medium of NC and KD-ATP6V0D1 HUVECs and cultured at 37°C for 1 h. Immunofluorescence images of two groups of HUVECs labeled against vWF (green) and nucleus (DAPI, blue) were shown. Scale bar, 10 μm. (F) The length of vWF strings at each group of HUVECs was measured by the NIH ImageJ software (n = 30 per group, ***p < 0.001). Data were expressed as mean ± SEM. Three independent experiments were performed.