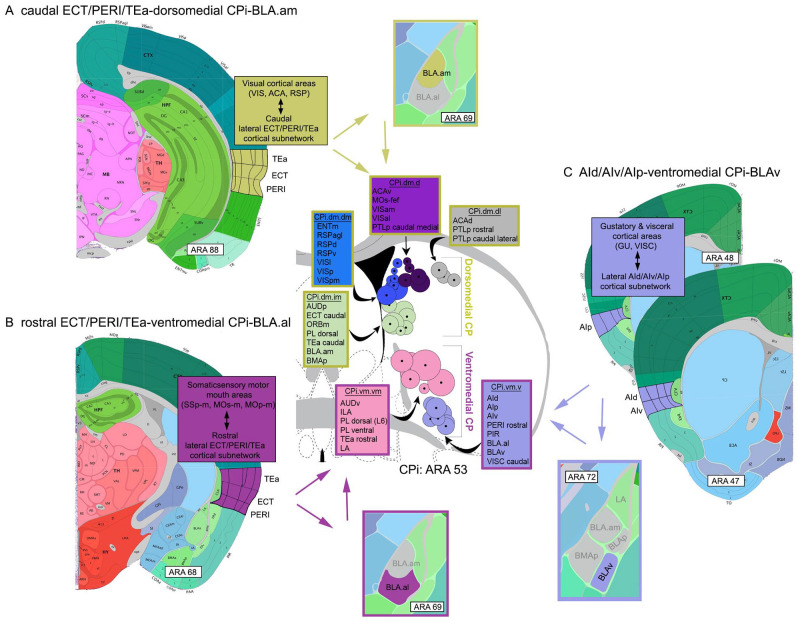
Figure 3.
Visual representations of cortico-striatal-BLA subnetworks. The intermediate CP (CPi) consists of 4 major divisions, each of which receives and integrates different cortical input. These are (1) the dorsomedial, (2) ventromedial, (3) dorsolateral, and (4) ventrolateral. Note that only the dorsomedial (yellow) and ventromedial (magenta) divisions are shown. Based on highly topographic cortico-striatal projections, each division can be subdivided into domains, smaller regions that receive convergent input from different cortical areas. Adjacent domains, particularly within a community, share integrated cortical information (for details, see Hintiryan et al 14 ). Each circle on the CPi denotes the center of terminations from a single cortical area. A group of color-coded circles represents a domain. Color-coded boxes list cortical areas that project to that domain (name of domain included, e.g., CPi.dm.dm). The stroke color of the boxes denotes the larger CPi division within which the domains interact (yellow: dorsomedial CPi; magenta: ventromedial CPi). (A) Visual representation of the caudal ECT/PERI/TEa-dorsomedial CPi-BLA.am subnetwork showing the interactions of these 3 regions potentially involved in visual information processing. At the cortical level, the caudal ECT/PERI/TEa is heavily interconnected with visual processing areas. The caudal ECT/PERI/TEa project to the dorsomedial CPi (stroke colored yellow), which also receives input from a wide variety of visual processing cortical areas. It also is the region of the CPi that BLA.am cells target. The caudal ECT/PERI/TEa also provides input to BLA.am. (B) Visual representations of the rostral ECT/PERI/TEa-ventromedial CPi-BLA.al subnetwork showing interactions among these three regions potentially involved in gustatory/visceral information processing. At the cortical level, the rostral ECT/PERI/TEa is heavily interconnected with somatic sensory motor regions that regulate the mouth. Rostral ECT/PERI/TEa project to the ventromedial CPi (stroke colored magenta), where cortical gustatory and visceral information is integrated. This is also the region in the CPi that BLA.al cells target. The rostral ECT/PERI/TEa also provides input to the BLA.al. (C) Visual representation of the AId/AIv/AIp-ventromedial CPi-BLAv subnetwork. The AId/AIv/AIp receives input from gustatory and visceral cortical areas and projects to the ventromedial CPi, which also receives input from cortical regions that process the same type of information. The BLAv also projects to the same CPi region and the AId/AIv/AIp project to the BLAv.
Abbreviations: ACA, anterior cingulate cortex; AId, agranular insular cortex, dorsal part; AIp, agranular insular cortex, posterior part; AIv, agranular insular cortex, ventral part; AUD, auditory cortex; CPi, intermediate caudoputamen; d, dorsal; ECT, ectorhinal cortex; ENT, entorhinal cortex; GU, gustatory cortex; i, intermediate; l, lateral; m, medial; ORB, orbitofrontal cortex; PERI, perirhinal cortex; PIR, piriform cortex; PTLp, posterior parietal association areas; RSP, retrosplenial cortex; TEa, posterior temporal association cortex; v, ventral; VIS, visual cortex; VISC, visceral cortex.