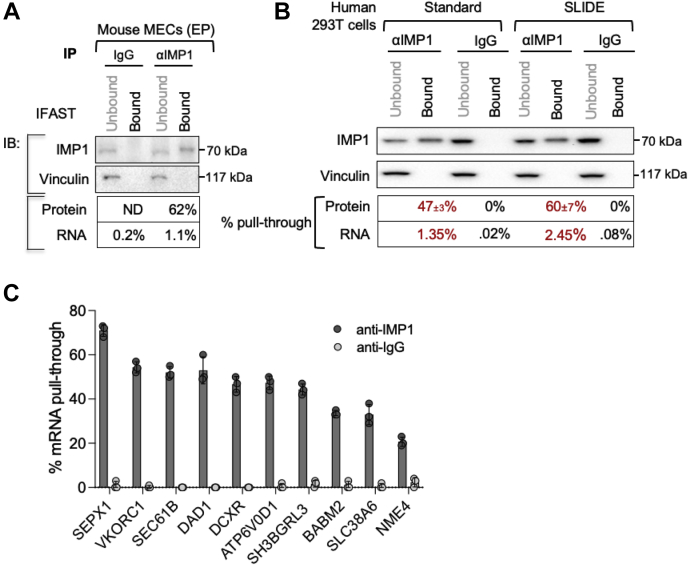
Figure 5.
Immunoprecipitation of RNA in RIP IMP-1 complexes isolated by ESP methods.A, determination of amount of RNA in IFAST–RIP. Mouse mammary epithelial (EP) cell lysates were incubated with anti-IMP-1 antibody or an IgG control, and immunoprecipitates were purified using IFAST–RIP. The protein component of the immunoprecipitate was analyzed by Western blotting as in Figure 4. RNA was purified, and the amount of RNA in each fraction was determined (n = 3). B, side-by-side comparison of RNA purification by standard and SLIDE–RIP. 293T cell lysates were incubated with anti-IMP-1 1° Ab or an IgG control, and lysate + antibody mixtures were purified using either standard or SLIDE-based RIP. The efficiency of pull through of IMP-1 (n = 3) and associated RNAs (n = 2) is shown. C, validation of SLIDE-enriched mRNA partners. Selected RNA species identified in FLAG-tagged IMP-1-associated RNP particles by Jonson et al. (38) were evaluated by qPCR of SLIDE-enriched RIP fractions of endogenous IMP-1 from 293T cells (n = 3). Ab, antibody; ESP, Exclusion-Based Sample Preparation; IFAST, Immiscible Filtration Assisted by Surface Tension; IgG, immunoglobulin G; IMP-1, insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein-1; qPCR, quantitative PCR; RIP, RNA immunoprecipitation; SLIDE, Sliding Lid for Immobilized Droplet Extractions.