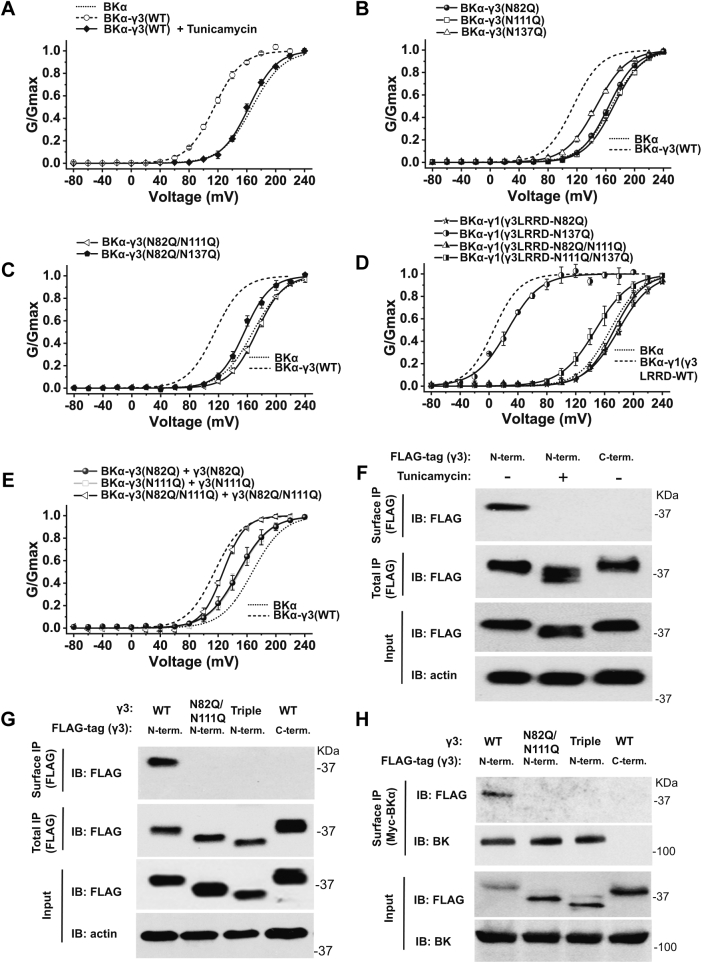
Figure 7.
Effects of N-glycosylation on the channel-modulation function and surface expression of the γ3 subunit.A, voltage dependence of BK channel activation for channels formed by cotranslational expression of BKα with γ3 WT protein in the absence and presence of cell treatment with tunicamycin. B and C, voltage dependence of BK channel activation for channels formed by cotranslational expression of BKα with (B) γ3 N82Q, N111Q, or N137Q mutant or (C) N82Q/N111Q or N82Q/N137Q double-site mutant. D, voltage dependence of BK channel activation for channels formed by cotranslational expression of BKα with γ1(γ3LRRD) chimeric protein’s N82Q, N137Q, N82Q/N111Q, or N111Q/N137Q mutant. E, voltage dependence of BK channel activation for channels formed by cotranslational expression of BKα with the γ3 N82Q, N111Q or N82Q/N111Q supplemented with overexpression of the corresponding γ3 mutant. F, immunoprecipitation of γ3 WT on the cell surface and whole-cell lysate from cells that had been treated with or without tunicamycin. G, immunoprecipitation of γ3 WT, double-site (N82Q/N111Q), and triple-site mutants on the cell surface (surface IP) and whole-cell lysate (total IP). H, coimmunoprecipitation of BKα and γ3 WT, double-site (N82Q/N111Q), and triple-site mutants on the cell surface. Immunoprecipitation was performed with a rabbit polyclonal anti-FLAG to pull down the FLAG-tagged γ3 subunit (F and G) or a rabbit polyclonal anti-Myc to pull down the Myc-tagged BKα subunit (H).