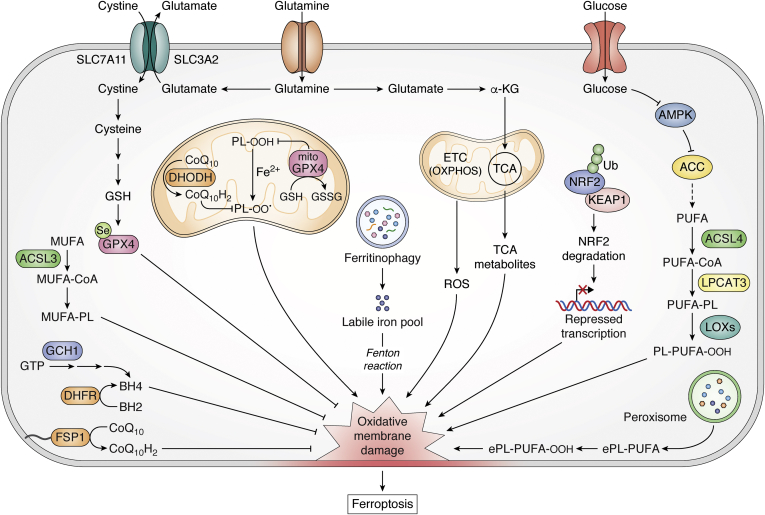
Figure 2.
Additional pathways governing the intrinsic regulation of ferroptosis. Several cell-autonomous or intrinsic mechanisms modulate cancer cell sensitivity to ferroptosis. This nonexhaustive list includes metabolic pathways that regulate PUFA and MUFA levels, mitochondria respiration and bioenergetics, ferritinophagy, NRF2 antioxidant system, and other direct lipid peroxide neutralizing pathways, e.g., FSP1 and DHODH, which are independent and parallel to GSH-GPX4. αKG, alpha ketoglutarate; ACC, Acetyl-CoA carboxylase; ACSL3, acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 3; ACSL4, acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4; AMPK, 5′ adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; BH2, dihydrobiopterin; BH4, tetrahydrobiopterin; CoA, coenzyme A; CoQ10, Coenzyme Q10; CoQ10H2, Coenzyme Q10 or ubiquinol; DHODH, dihydroorotate dehydrogenase; DHFR, dihydrofolate reductase; ePL-PUFA, ether phospholipid-polyunsaturated fatty acids; ETC, electron transport chain; FSP1, ferroptosis suppressor protein1; GCH1, GTP cyclohydrolase 1; GPX4, glutathione peroxidase 4; GPX4mito, mitochondrial GPX4; GSH, glutathione (reduced); GSSG; glutathione (oxidized); KEAP1, Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; LIP, labile iron pool; LOXs, lipoxygenases; LPCAT3, lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3; MUFA, monounsaturated fatty acid; MUFA-PL, monounsaturated fatty acid phospholipid; NRF2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; OXPHOS, oxidative phosphorylation; PLOO, phospholipid hydroperoxyl radical; PLOOH, phospholipid hydroperoxide; PUFA, polyunsaturated fatty acid; PUFA-PL, polyunsaturated fatty acid phospholipid; ROS, reactive oxygen species; Se, Selenium; TCA, tricarboxylic acid cycle; Ub, Ubiquitin.