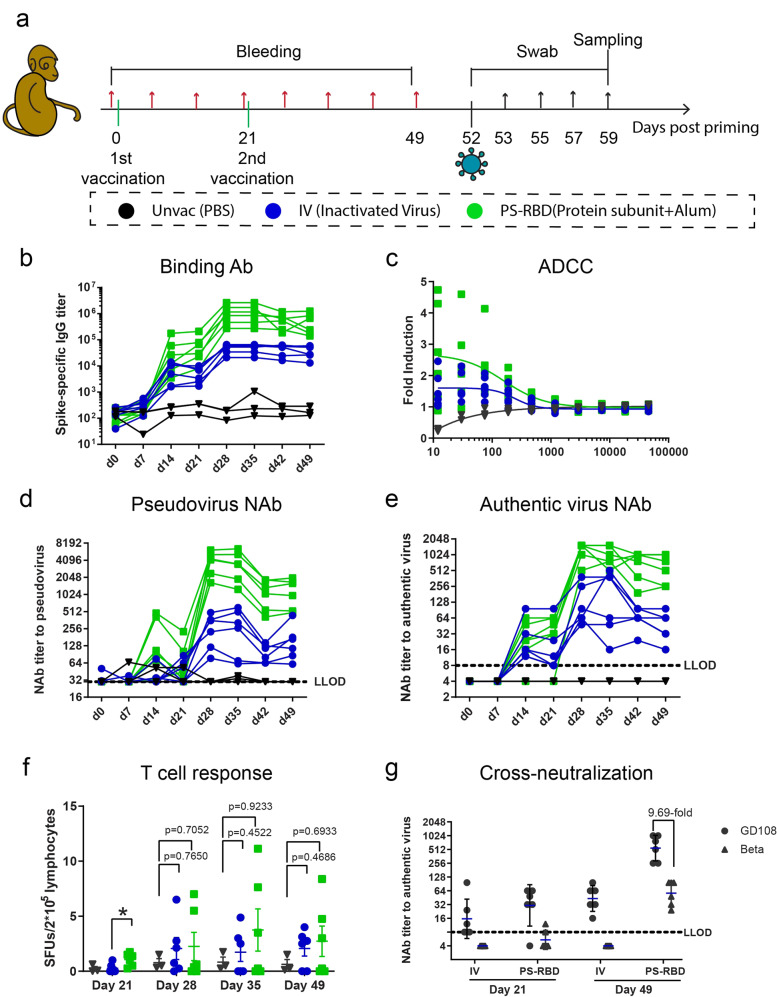
Fig. 1.
Immune responses induced by PS-RBD and positive control. a Schematic representation of the experimental protocol. Female rhesus macaques were randomly classified into 3 groups and immunized with 2 doses of PBS (Unvac, n = 3), inactivated virus vaccine (IV, n = 6), or RBD targeting protein subunit vaccine (PS-RBD, n = 6). “Unvac” was set as the blank control. For all NHPs, blood was collected before immunization and every 7 days post priming. On day 52, NHPs were challenged with Beta variant (B.1.351). Nasal swabs were collected at a dedicated time point as shown, and all NHPs were sacrificed on day 7 post challenge for the collection of the trachea, lung, and BALs. b–e Humoral immune responses, including the dynamic titer of sera spike protein-specific IgG (b), ADCC effect on day 42 (c), dynamic NAb titer measured by pseudovirus (d), and live prototype strain GD108 (e). Levels of ADCC were expressed as fold induction of relative light unit; NAb titers were expressed as 50% effective dilution (ED50) of serum. f Spike-specific T cell responses of PBMC were measured by IFN-γ ELISPOT assay and expressed as spot-forming units per 2 × 105 lymphocytes. g Cross-neutralizing activity of sera to prototype (GD108) and Beta (B.1.351) is expressed as ED50. One spot represents one animal. Bars represent the mean ± SEM