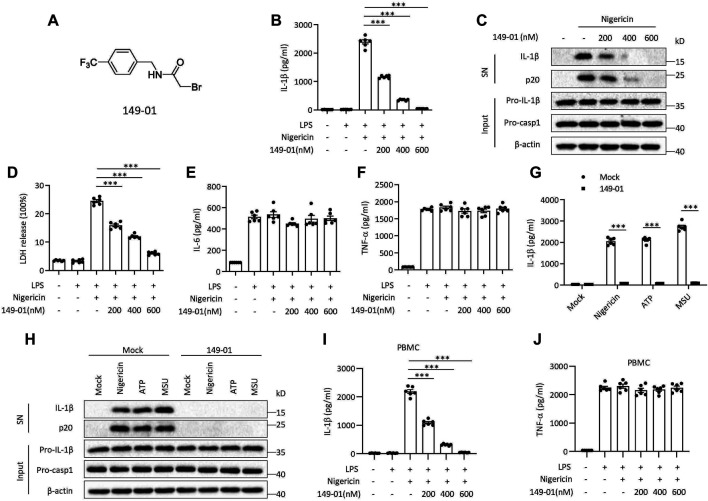
FIGURE 1.
Identification of 149-01 as a highly potent inhibitor for NLRP3 inflammasome. (A) 149-01 structure. (B–F) BMDMs were first primed with LPS for 3 h, then pretreated with indicated doses of 149-01 (200-600 nM) for 30 min, lastly stimulated with nigericin. (B) IL-1β releases in supernatants were detected by ELISA. (C) Active IL-1β and p20 (cleaved caspase-1) in supernatants (SN) and pro-IL-1β, pro-caspase-1 and β-actin in cell lysates (Input) were measured by western blot. (D) The release of LDH in supernatants. (E) IL-6 and (F) TNF-α secretion levels in supernatants were determined by ELISA. (G,H) BMDMs were first primed with LPS, then treated with or without 149-01 (600 nM) for 30 min, lastly stimulated with nigericin, ATP or MSU. (G) IL-1β releases in supernatants were detected by ELISA. (H) Active IL-1β and p20 in supernatants and pro-IL-1β, pro-caspase-1 and β-actin in cell lysates were measured by western blot. (I,J) PBMCs were first primed with LPS for 3 h, then pretreated with indicated doses of 149-01 for 30 min, lastly stimulated with nigericin. (I) IL-1β and (J) TNF-α secretion levels in supernatants were determined by ELISA. Data are obtained from three independent experiments, each with two biological replicates and are expressed as mean ± s. e.m (n = 6) (B,D–G,I,J), or are representative of three independent experiments (C,H). One-way ANOVA was applied to calculate statistical significance: ***p < .001.