Figure 6. ZFP207 is a novel RBP.
-
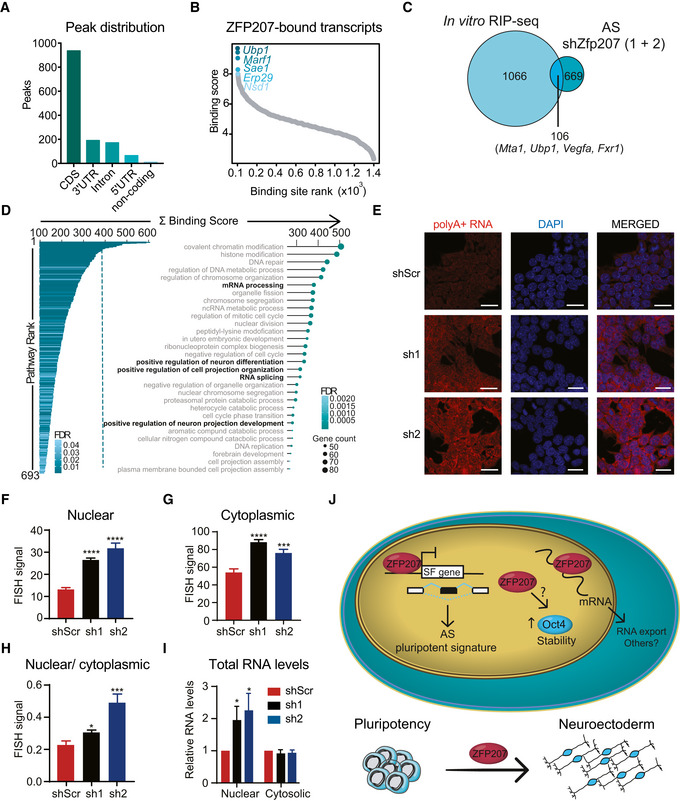
A–D(A) Distribution of ZFP207‐binding sites across common transcript features. (B) Scatterplot depicting ranked distribution of ZFP207 binding sites. The top 5 strongest binding sites are highlighted. (C) Venn diagram of in vitro RIP‐seq and AS upon Zfp207 knockdown. (D) Bar‐ and dot plots show significantly enriched GO terms for biological processes for ZFP207 bound genes. Top 30 GO terms are shown.
-
E–I(E) FISH of poly(A)+ RNA distribution in shScr, sh1 and sh2 stained with 5′Cys3‐oligo dT(50). Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. Scale bar, 20 µM. Quantification of (F) nuclear, (G) cytoplasmic, and (H) of nuclear/cytoplasmic poly(A)+ FISH signals. (I) Relative nuclear and cytosolic total RNA levels in sh1 and sh2 compared to shScr. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of n ≥ 3 independent biological experiments. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 (shScr versus sh1 or sh2); unpaired Student’s t‐test.
-
JZFP207 modulates mouse ESCs pluripotency and neuroectodermal differentiation by integrating co‐ and post‐transcriptional mechanisms.
