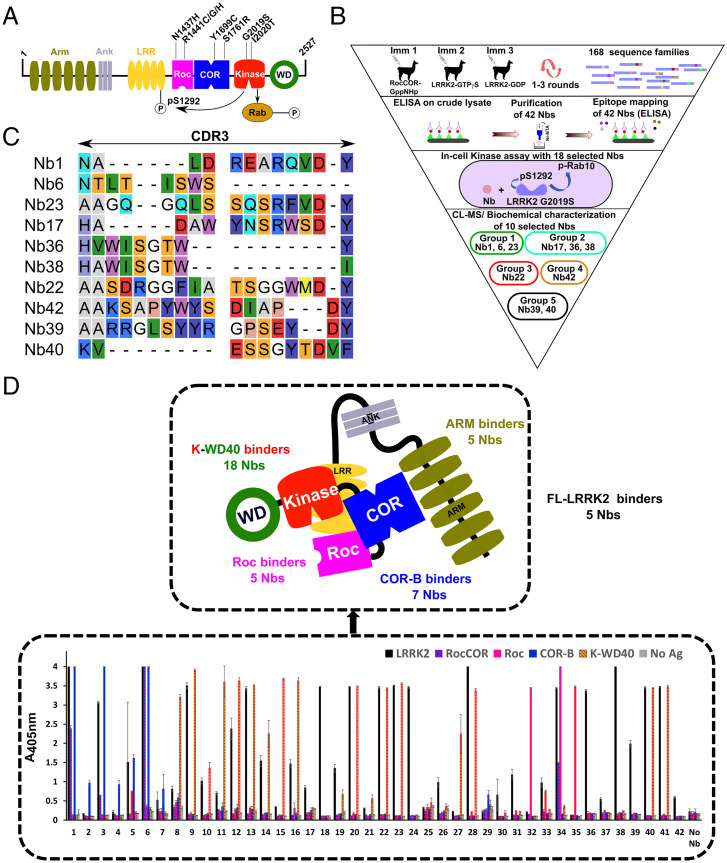
Fig. 1.
Identification of LRRK2-targeting Nbs. (A) Domain arrangement of LRRK2, with important PD mutations indicated. Two LRRK2 kinase activities relevant to this study are also indicated: phosphorylation of Rab proteins and autophosphorylation at position S1292. (B) Funnel approach used in this study to identify and characterize LRRK2-binding and modulating Nbs. The 10 Nbs that are characterized in detail are categorized into five functional groups: group1, inhibit all LRRK2 kinase activities (dark green); group 2, specifically inhibit LRRK2 Rab phosphorylation (light green); group 3, activate LRRK2 kinase (red); group 4, inhibit LRRK2 activity in cells (orange); and group 5, no effect on LRRK2 activity (black). (C) Sequences of the CDR3 regions of the 10 Nbs that were analyzed in detail. Nb36 and Nb38 belong to the same CDR3 sequence family. (D, Lower) Domain mapping of the purified Nbs using ELISA on either FL-LRRK2, the RocCOR, Roc, COR-B, or K-WD40 constructs. The Nbs that only show binding to FL-LRRK2 were additionally tested for binding on the RCKW and ARM domain constructs (SI Appendix, Fig. S3). Each ELISA signal is the average of three experiments. (Upper) The results of both of these domain-mapping experiments are schematically shown.