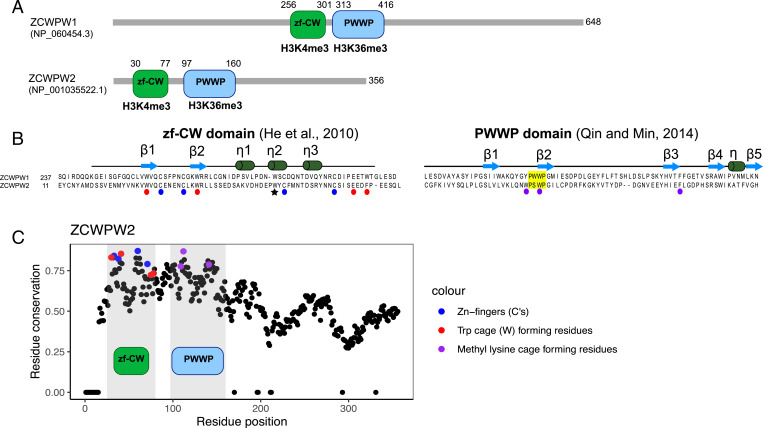
Fig. 4.
Domain architecture ZCWPW1 and ZCWPW2. (A) Amino acid sequence and domain structure composition of genes ZCWPW1 and ZCWPW2 in humans. (B) The ZF-CW domain structure includes the fingers (residues indicated by blue circles) and an aromatic cage (red) expected to bind to H3K4me3 (61), and the star indicates the third Trp residue that is thought to stabilize the fold by hydrophobic interactions (61). The PWWP domain (yellow) is expected to bind to histone H3K36me3 through a hydrophobic cavity composed of three aromatic residues (purple) (62). The secondary structures of zf-CW and PWWP domains are represented above sequences. (C) Conservation of residues in ZCWPW2 across vertebrates, with those residues recognizing modifications on the histone tail colored in blue, red and purple. Positions in the ZCWPW2 alignment with >30% of gaps were ignored, and the conservation score was set to 0. A similar plot for the conservation of residues in ZCWPW1 was previously reported (figure 1B in Ref. 27).