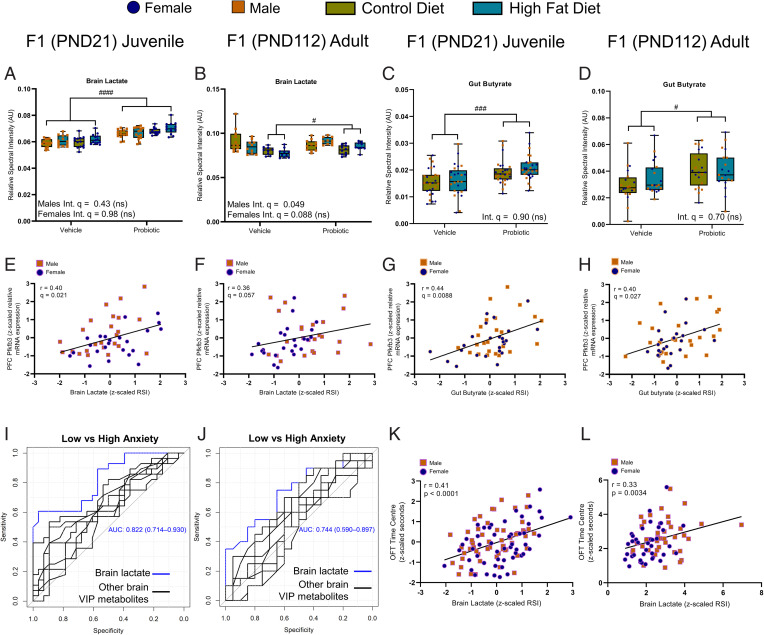
Fig. 8.
Key gut and brain metabolites altered by maternal probiotic treatment show correlations with a genetic marker of astrocytic metabolism and anxiety behavior. (A) In the juvenile offspring, two-way ANOVA revealed that maternal probiotic treatment increased brain lactate levels in both male [main effect, F(1,53) = 44.57] and female [main effect, F(1,48) = 60.07] relative to vehicle. (B) In the adult male offspring, there was a significant maternal diet × probiotic treatment interaction [F(1,38) = 5.32] for brain lactate. Note that post hoc Tukey analysis did not identify significant group differences (P > 0.05). In the adult female offspring, maternal probiotic intake increased brain lactate independent of diet [F(1,34) = 6.97]. Maternal probiotic treatment increased gut butyrate levels in both the juvenile offspring [main effect, F(1,101) = 13.83] (C) and the adult offspring [F(1,72) = 8.71] (D) independent of maternal diet and sex. A significant correlation (Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient) between brain lactate levels and PFC PFKFB3 expression was found for juvenile (r = 0.40, n = 48 [24F, 24M]) (E), but not for adult (r = 0.36, n = 48 [24F, 24M]) (F), offspring. Correlations for gut butyrate and PFC PFKFB3 expression were found for both juvenile (r = 0.44, n = 48 [24M, 24F]) (G) and adult (r = 0.40, n = 48 [24M, 24F]) (H) offspring. Receiver operating characteristic curves (I, juvenile; J, adult) for brain lactate concentration compared to other discriminatory brain metabolites as classifiers for high and low anxiety-like behavior in the OFT in juvenile (n = 28 low anxiety [10M, 18F], 28 high anxiety [15M, 13F]) and adult (n = 20 low anxiety [12M, 8F], high anxiety [5M, 15F]) offspring, respectively. Significant correlations between brain lactate levels and OFT time in center were found for juvenile (r = 0.41, n = 111 [57M, 54F]) (K) and adult (r = 0.33, n = 80 [42M, 38F]) (L) offspring. (A–D) n = 13 to 15 juvenile offspring, n = 9 to 11 adult offspring per sex per group. Data are presented as boxplots showing median, interquartile range, and min/max points. AU, arbitrary units; Int., interaction; ns, not significant. #P < 0.05; ###P < 0.001; ####P < 0.0001 (indicating main effect of maternal probiotic treatment). Where sex differences occurred, separate two-way ANOVAs were performed.