Figure EV1. MBELN‐induced induction of AhR.
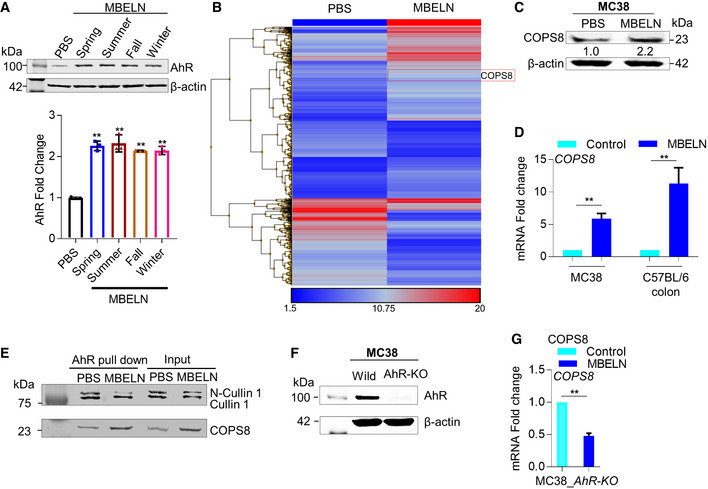
- To test the reproducibility of mulberry bark‐derived exosome‐like nanoparticles (MBELN) collected during different seasons of the year, MBELNs were extracted in spring, summer, fall, and winter and used to treat MC38 cells to evaluate AhR expression. Data are mean ± SEM from three biological replicates per group. **P < 0.01 using one‐way ANOVA.
- Heat map showing gene influences in crypts of villi in C57BL/6J mice. Data shown are from three technical replicates.
- Western blot for COP9/COP9 Constitutive Photomorphogenic Homolog Subunit 8 (COPS8) in MC38 cells following MBELN treatment. Data shown are from three biological replicates.
- mRNA expression of COPS8 in MC38 and after MBELN administration and C57BL/6J colon epithelial cells following MBELN administration for 7 days. Data are mean ± SEM from three biological replicates per group. **P < 0.01 using Student’s t‐test.
- MC38 cells treated with MBELN and protein extract were immunoprecipitated using anti‐aryl hydrocarbon receptors (AhR) antibody. The precipitate was subjected to Western blot with antibody against Cullin 1 (CUL1) and COPS8. Data shown are from three biological replicates.
- Western blot to confirm knockout of AhR in MC38 cells. Data shown are from three biological replicates.
- COPS8 mRNA expression in AhR‐knockout (AhR‐KO) MC38 cells following treatment with MBELNs. Data are mean ± SEM from three biological replicates per group. **P < 0.01 using Student’s t‐test.
Source data are available online for this figure.
