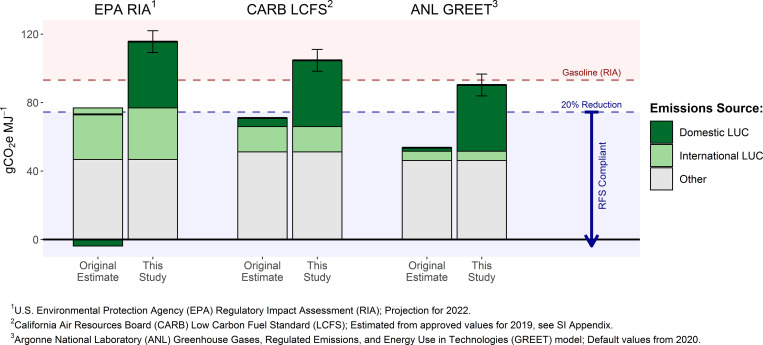
Fig. 3.
GHG emission intensities for corn ethanol with and without updated domestic LUC emissions. Original estimates reflect GHG intensities of corn ethanol according to the US EPA RIA [projection for 2022 (35)], California Air Resources Board (CARB)’s Low Carbon Fuel Standard (LCFS) [estimated from approved values for 2019 (62); SI Appendix], and Argonne National Laboratory (ANL)’s Greenhouse Gases, Regulated Emissions, and Energy Use in Technologies (GREET) model [default values for 2020 (63)]. Revised estimates (this study) replace the estimated domestic LUC emission from each source with those identified in this study. Our domestic LUC emissions estimate includes ecosystem carbon losses (including methane) from land conversion and on-site nitrous oxide emissions from additional fertilizer usage but excludes all other upstream and downstream emissions. Error bars represent 95% CIs for emissions from domestic LUC only (SI Appendix).