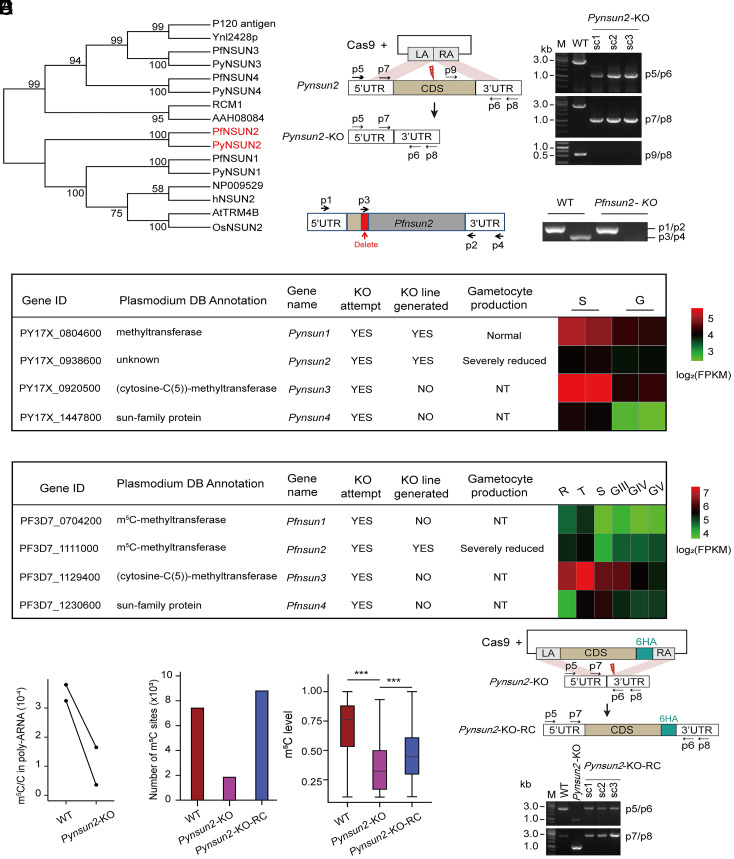
Fig. 3.
Identification and verification of PyNSUN2 as a m5C methyltransferase. (A) Phylogenetic analysis of candidate NSUN m5C methyltransferases in P. yoelii and P. falciparum. Sequences were aligned using ClustalX 2.1. The neighbor-joining phylogeny was performed using MEGA 5.2.2 with 1,000 replicates. (B) Strategies to generate Pynsun2-KO and Pfnsun2-KO parasites. For CRISPR/Cas9-mediated deletion of the Pynsun2 CDS, the left arm (LA) and right arm (RA) were designed to match sequences in the 5′ UTR and 3′ UTR of Pynsun2, respectively. For disruption of Pfnsun2, sgRNA targeting was used to delete a portion of the CDS (red box) and introduce multiple stop codons downstream. Red thunderbolt indicates the site for sgRNA targeting. PCR products with indicated primer pairs confirmed the expected differences between the WT and allelically manipulated parasites (single clones: sc1–3, with the expected amplicon sizes; p5/p6: 1.1 kb for the Pynsun2-KO vs. 2.7 kb for WT parasites; p7/p8: 1 kb for Pynsun2-KO vs. 2.6 kb for WT). Sequence data confirming the deletion and stop codons in the Pfnsun2-KO parasites are shown in SI Appendix, Fig. S4A. (C) Summary results from experiments to disrupt homologs of the NSUN family in P. yoelii and P. falciparum. NT: not tested. Heatmaps show transcript fragment abundance levels from each gene in the WT parasites, as determined by RNA-seq. (D) LC-MS/MS-determined levels of m5C/C in the poly(A)-selected transcripts of P. yoelii WT and Pynsun2-KO parasites (schizont stage). Paired points represent the results of each of two biological replicates showing an average 72% reduction (P = 0.046 by paired t test). (E) Histogram shows numbers of mRNA m5C sites in schizont stages of WT, Pynsun2-KO and Pynsun2-KO-RC P. yoelii clones. Box plot shows the corresponding m5C levels in WT, Pynsun2-KO, and Pynsun2-KO-RC lines (Right) (***P < 0.001, Wilcoxon test). Only m5C sites detected in both replicates were used for the graphs. (F) Strategy for genetic complementation repair of the Pynsun2-KO with the gene CDS fused with a C-terminal 6HA. (Upper) The design for the CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene knockin. LA and RA match sequences in the 5′ UTR and 3′ UTR of Pynsun2, respectively. Red thunderbolt indicates the site for sgRNA targeting. (Lower) The expected PCR products from three Pynsun2-KO-RC clones (sc1–3) by the primer sets p5/p6 (1.1 kb for the Pynsun2-KO line vs. 2.7 kb for the WT and Pynsun2-KO-RC lines) and p7/p8 (1 kb for the Pynsun2-KO vs. 2.6 kb for the WT and Pynsun2-KO-RC lines).