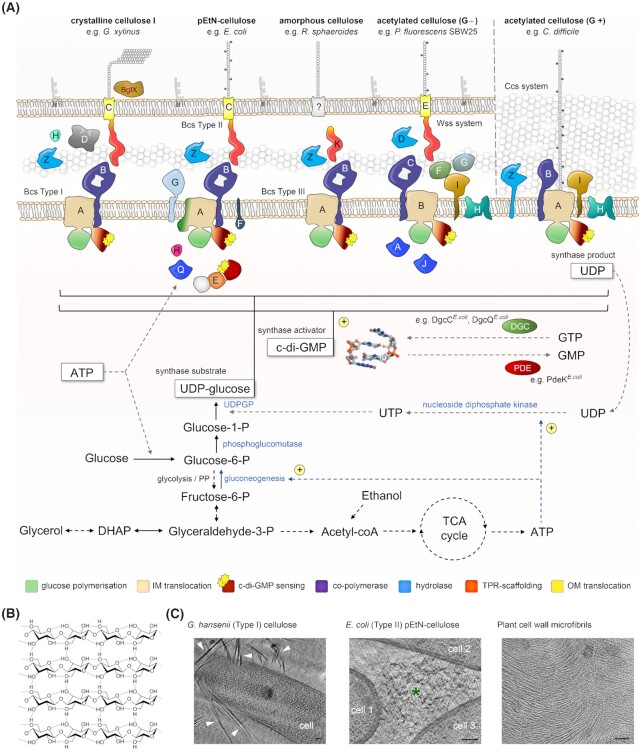
Figure 1.
Bacterial cellulose secretion. (A)Prevalent types of bacterial cellulose secretion systems and associated metabolic processes. UDPGP: UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase, also called UTP–glucose-1-phosphate uridylyl transferase or GalU; UDP: uridine diphosphate; ATP: adenosine triphosphate; PP: pentose-phosphate pathway; DHAP: dihydroxyacetone phosphate; TCA cycle: tricarboxylic acid cycle; c-di-GMP: cyclic diguanosine monophosphate; PDE: phosphodiesterase; DGC: diguanylate cyclase. (B) Inter- and intrastrand hydrogen bonding in crystalline cellulose I. Image by Luca Laghi, reproduced under license CC BY-SA 3.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/legalcode). (C) Cryo-electron micrographs of secreted bacterial and plant cellulose. Data: courtesy of William J. Nicolas, partially reported in (Nicolas et al. 2021) and reproduced under the CC BY 4.0 license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/legalcode). Left: a biofilm-embedded Gluconacetobacter hansenii cell surrounded by crystalline cellulose ribbons (marked by white arrowheads); middle: amorphous phosphoethanolamine (pEtN)-cellulose (marked by an asterisk), secreted by the commensal Escherichiacoli 1094 strain; right: plant cellulose microfibrils observed as electron-dense filaments in onion cell wall in situ. Scale bars: 100 nm.