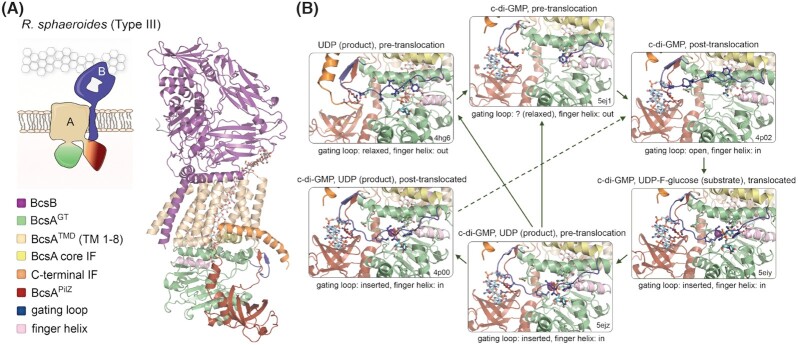
Figure 2.
The BcsAB catalytic complex.(A) Thumbnail representation and crystal structure of the 1:1 BcsAB tandem from R. sphaeroides. A co-purified cellulose polymer is shown in sticks (pdb 4p02) (Morgan, McNamara and Zimmer 2014). TMD: transmembrane export domain; IF: interface helix; GT: glycosyltransferase domain. (B) Zoom-in of the synthase active site as captured in the crystal structures of the R. sphaeroides BcsAB tandem from crystals grown or incubated with different ligands. Color coding as in panel (A). Protein data bank accession numbers, as well as the presence of substrate homologs, products, c-di-GMP, translocation state of the polymer and gating loop conformation are indicated for each state (Morgan, Strumillo and Zimmer 2013; Morgan, McNamara and Zimmer 2014; Morgan et al. 2016). Green arrows indicate putative conformation transition pathways integrating all captured conformational states. Alternative pathways would depend on local c-di-GMP, product and substrate concentrations, as well as finger helix-mediated or spontaneous translocation. The cellulose polymer, substrate homolog, UDP product, c-di-GMP and key residues from the gating loop, c-di-GMP coordinating PilZ-proximal linker, finger helix and conserved QRGRW motif are shown as sticks.