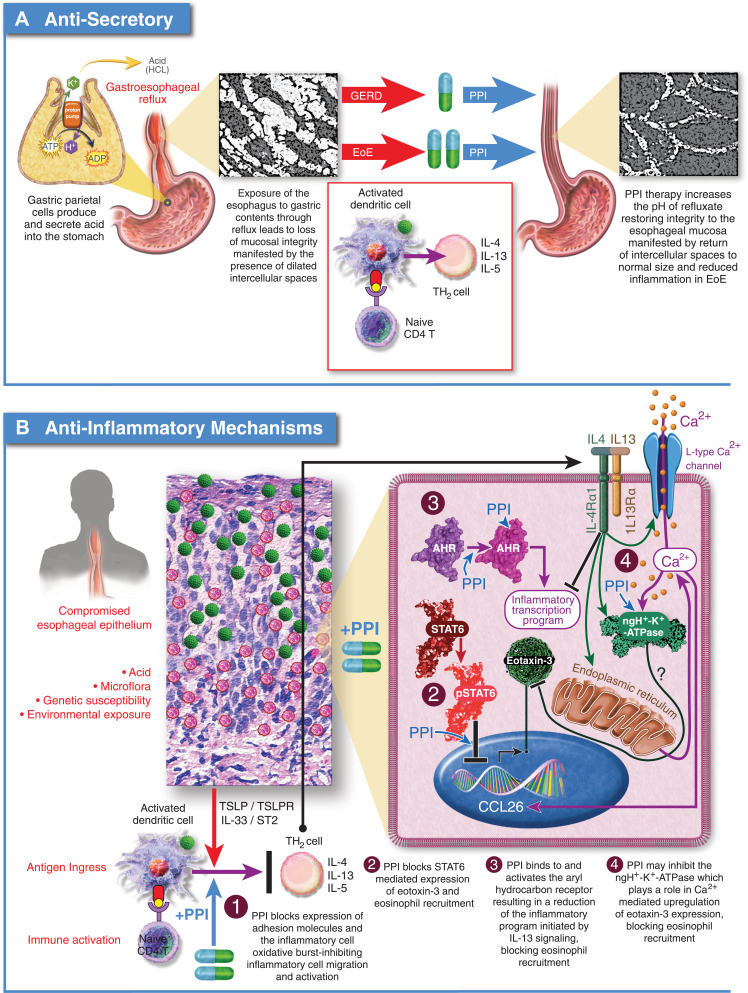
Figure 3.
Proposed mechanisms of PPI efficacy for EoE. (A) Anti-Secretory Mechanism: Hypothesizes that the integrity of the esophageal epithelium is compromised by exposure to gastric acid leading to ingress of antigens and activation of an immune response. Acid suppression by PPIs allows the esophageal epithelium to heal facilitating resolution of inflammation. (B) Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms: 1.) PPIs block expression of cell surface adhesion molecules, inhibiting migration of inflammatory cells to the esophageal epithelium; 2.) PPIs block STAT6 mediated expression of eotaxin-3 reducing recruitment of eosinophils to the esophageal epithelium; 3.) PPIs can stimulate the aryl hydrocarbon receptor normalizing expression of genes involved in barrier function including, filaggrin, loricrin, and involucrin through inhibition of the IL-4/IL-13-STAT6 pathway; 4.) PPIs can inhibit the activity of ATP12A, the non-gastric P2-type H+, K+-ATPase. IL-4 mediated induction of eotaxin-3 secretion is sensitive to inhibition of ATP12A.