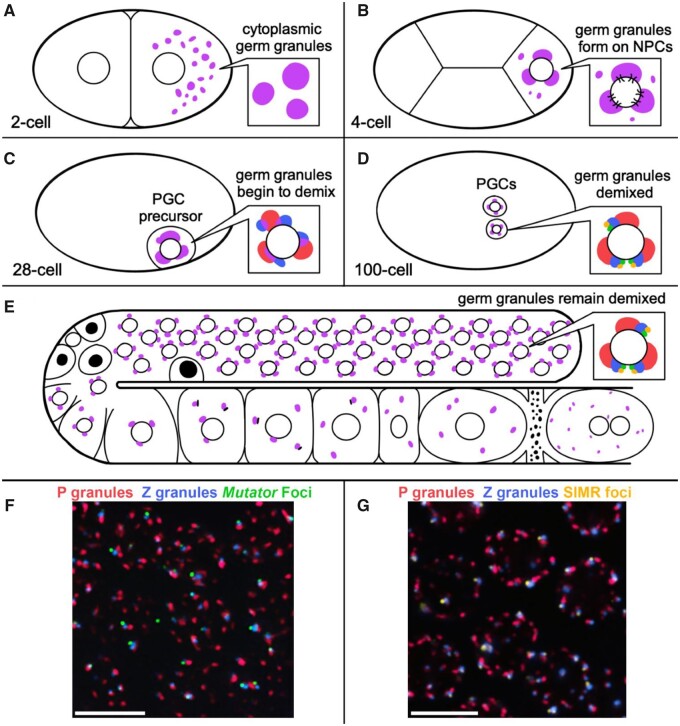
Figure 1.
Germ granule distribution and demixing during development. (A) Posteriorly localized germ granules (purple) in the 2-cell embryo are dispersed in the cytoplasm. (B) Germ granules in the 4-cell embryo begin to adhere to the cytoplasmic surface of the nuclear envelope and cluster NPCs. (C) Germ granule demixing begins at the 28-cell stage in primordial germ cell (PGC) precursors. (D) Germ granules in the PGCs of 100-cell embryos have demixed into adjacent P granules, Z granules, SIMR foci and Mutator foci. (E) Germ granules remain demixed in adult germ cells (inset). PGL proteins, but not GLH proteins, are cleared from P granules during physiological apoptosis (black nuclei). P granules disperse into the cytoplasm of oocytes prior to fertilization, initially with part of the nuclear envelope attached. (F, G) Immunofluorescence image of adult germ cells (pachytene) with demixed sub-granules. (images Celja Uebel. scale bars = 5 μm).