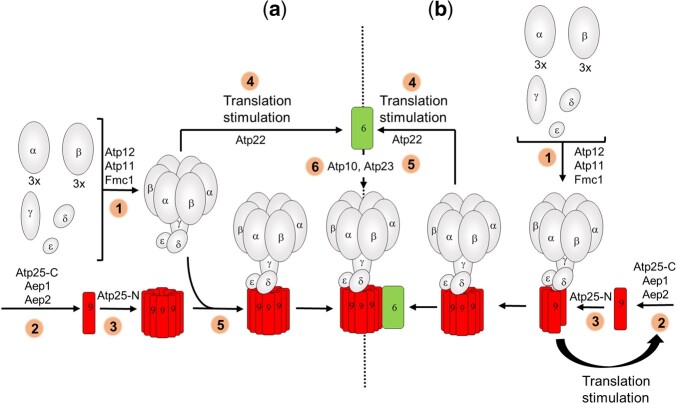
Fig. 8.
Model of assembly-dependent translation of subunits 6 and 9 of yeast ATP synthase. a) Previously reported model (Rak et al. 2009, 2011). 1: The subunits of F1 (α, β, γ, δ, ε) assemble with the help of Atp11, Atp12, and Fmc1. 2 and 3: The subunit 9 is produced and assembled with the help of Aep1, Aep2, Atp25-C, and Atp25-N independently of any other ATP synthase component. 4: The F1 alone is involved in the activation of subunit 6 translation by Atp22. 5: The F1 and the 910-ring associate to each other. 5: The subunit 6 with the help of Atp10 and Atp23 is incorporated into ATP synthase. b) Model based on the results reported in this study. 1: The subunits of F1 (α, β, γ, δ, ε) assemble with the help of Atp11, Atp12 and Fmc1. 2, 3: The synthesis and assembly of subunit 9 with the help of Aep1, Aep2, Atp25-C, and Atp25-N is F1-dependent. 4: The F1-910 intermediate stimulates translation of subunit 6 by Atp22. 5: The subunit 6 with the help of Atp10 and Atp23 is incorporated into ATP synthase. The peripheral stalk subunits 8, 4, i, j, f, d, and OSCP of the ATP synthase monomer are not represented.