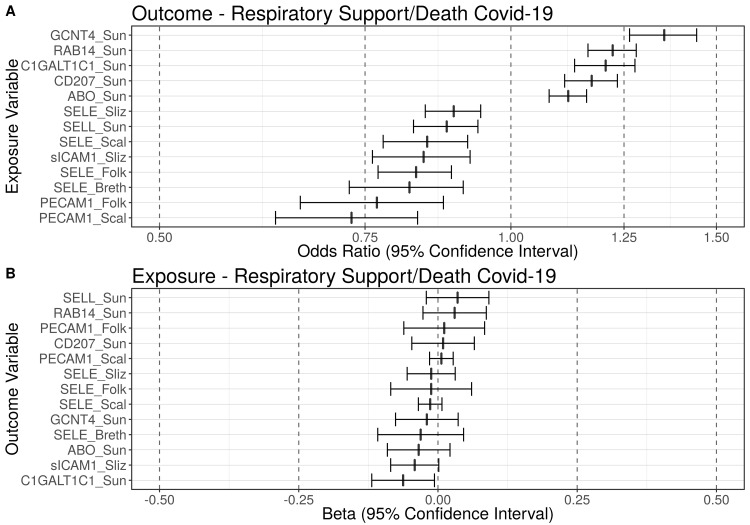
Fig 2. Blood markers putatively causally associated with need for respiratory support/death due to COVID-19.
Summary figure of the false discovery rate-corrected (pFDR = 0.05) Mendelian randomization results using the Generalised Summary data-based Mendelian randomization (GSMR) method. Using genetic instruments and under the assumptions of Mendelian randomization, this figure displays: (A) Summary figure when respiratory support/death-COVID-19 is the outcome of interest; (B) Summary figure when respiratory support/death-COVID-19 is the exposure of interest. Odds ratios (ORs) of blood markers causally associated with the need for respiratory support/death due to COVID-19 are displayed on the x-axis (with 95% confidence intervals). The blood markers are displayed on the y-axis. The dashed line at one represents an odds ratio of one (i.e., no effect). Using genetic instruments and under the assumptions of Mendelian randomization, five blood markers were causally associated with a significantly increased risk for need for respiratory support/death due to COVID-19 and eight blood markers were causally associated with a significantly decreased risk for respiratory support/death (qFDR ≤ 0.05). ABO = ABO system transferase; C1GALT1C1 = C1GALT1 specific chaperone 1; CD207 = langerin; GCNT4 = glucosaminyl (N-Acetyl) transferase 4; LCTL = lactase-like protein; PECAM1 = platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule; RAB14 = ras-related protein rab-14; SELE = E-selectin; SELL = L-selectin; sICAM1 = soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1.