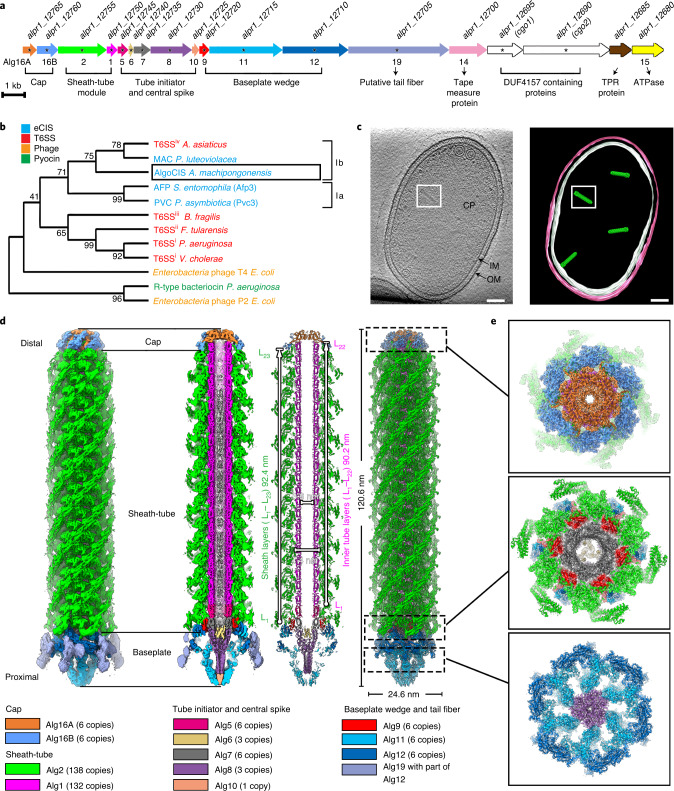
Fig. 1. Identification and characterization of a contractile injection system in A. machipongonensis.
a, Schematic showing the gene cluster of a putative contractile injection system in A. machipongonensis (AlgoCIS). The genes are labelled on the basis of similarities to AFP. Gene products that were detected by MS are marked by asterisks. The gene accession numbers are shown above the corresponding genes. b, Phylogenetic analyses based on putative sheath proteins showing that the closest relatives of AlgoCIS are MACs and T6SSiv, which belong to clade Ib CIS. The different representatives are colour-coded on the basis of their modes of action. c, Representative cryoET slice of A. machipongonensis cell (left) and the corresponding model (right), showing cytoplasmic AlgoCISs that are not attached to the inner membrane. CP, bacterial cytoplasm; IM/white, inner membrane; OM/pink, outer membrane; green, AlgoCIS particle. One representative AlgoCIS particle is marked with a white box. Shown is a 10.8 nm thick slice. Scale bars, 50 nm. In total, 38 tomograms were acquired. d, Shadowed surface (left) and ribbon (right) diagrams showing the overall cryoEM structure of AlgoCIS in the extended state (sliced views in the centre). Structural subunits are colour-coded according to the gene cluster in a. e, Perpendicular views of shadowed surface and ribbon diagrams showing the AlgoCIS model corresponding to the sections in d.