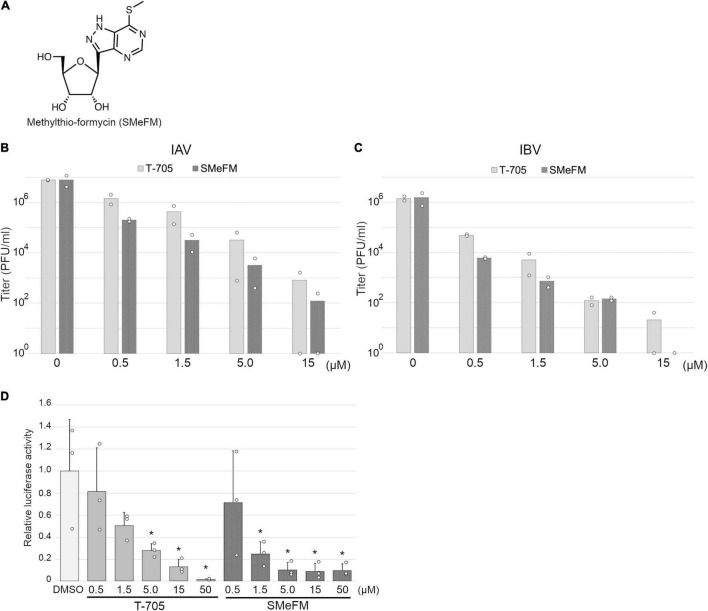
FIGURE 1.
Inhibition of influenza viral polymerase activity by methylthio-formycin (SMeFM). (A) Chemical structure of SMeFM. (B,C) Inhibition of influenza virus propagation by SMeFM. MDCK cells were infected with influenza A [WSN strain; (B)] or B [Lee strain; (C)] virus at an MOI of 0.01 PFU/ml and incubated with SMeFM or T-705 for 48 h. The virus titer in the supernatant was determined by plaque assay. The bar indicates the average titer of two independent experiments. The circles indicate the titer of each experiment. The circles of 100 are below the detection limit (<40 PFU/ml). (D) Viral polymerase activity in the presence of T-705 or SMeFM. Mini-replicon assay was performed by viral polymerase and NP derived from PR8. After 6 h transfection, SMeFM or T-705 was added to the cell culture medium and incubated for 18 h further. The graph indicates average values with standard deviations from three independent experiments. The circles indicate the relative luciferase activity of each experiment. P-values were calculated by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test. An asterisk indicates P-value less than 0.05.