Figure 4.
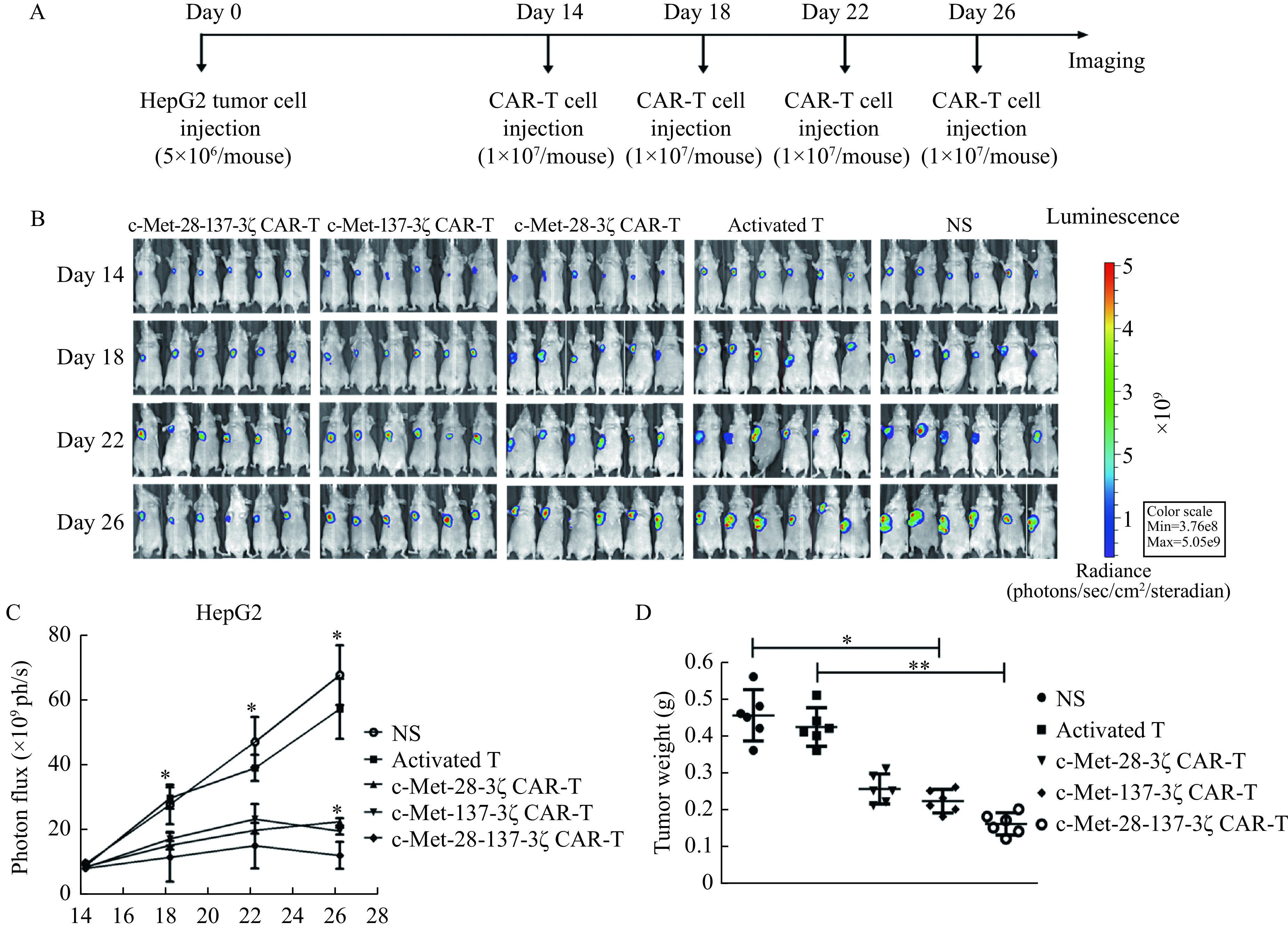
Anti-tumor efficacy of c-Met CAR-T cells in human HCC xenograft model.
A: Schematic representation the subcutaneous implantation of HepG2-Luc cells and treatment of c-Met CAR-T cells. BALB/c nude mice (n=6 for each group) were injected with 5×106 HepG2-Luc subcutaneously into the right underarm. A total of 1×107 c-Met CAR-T cells or activated T cells were injected subcutaneously around the tumor on days14, 18, 22 and 26, respectively. B: Serial tumor bioluminescence imaging of mice on the 14th, 18th, 22nd, and 26th days after the tumor cell injection. C: The tumor burden was assessed by total bioluminescence signals. D: At the end of the experiment, the tumor tissue was isolated and weighed. Statistical analyses were performed by one-way ANOVA for comparisons between multiple groups with a single variable (C and D). *P<0.05;**P<0.01. HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma; HepG2-Luc: HepG2 cells expressing luciferase. NS: 0.9% NaCl.
