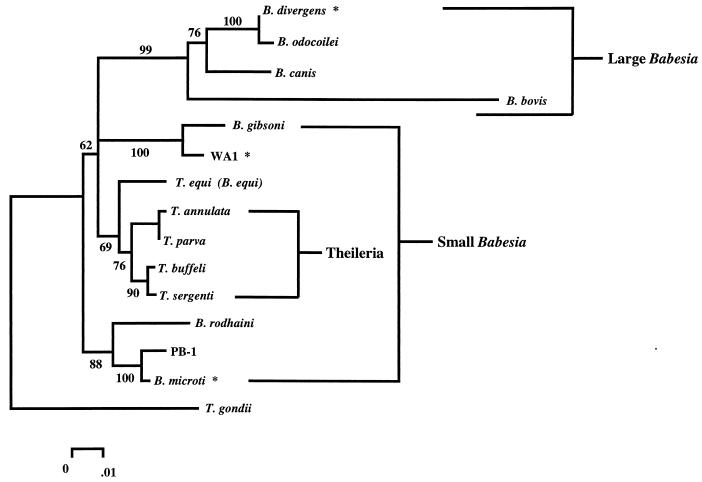
FIG. 2.
Phylogenetic tree representation of a neighbor-joining analysis of several species of piroplasms. Five hundred nucleotides of the nuclear small-subunit rDNA were aligned by using the Pileup program of the Wisconsin Genetics Computer Group package. Phylogenetic analysis of the alignment was performed as described previously (102) with the Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) computer program, version 1.01 (109), to make a Jukes-Cantor distance measurement and perform a neighbor-joining analysis with 500 bootstrap replicates. The phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (PAUP) computer program, version 3.1.1 (222), was used to confirm the order observed by the neighbor-joining analysis (using a branch-and-bound algorithm with 100 bootstrap replicates). The percentage of neighbor-joining bootstrap replications (>50%) is shown above each node. This tree is consistent with previously published analyses (160, 161). Species that are known to infect humans are marked with an asterisk. The groups of large and small babesias are bracketed and labeled.