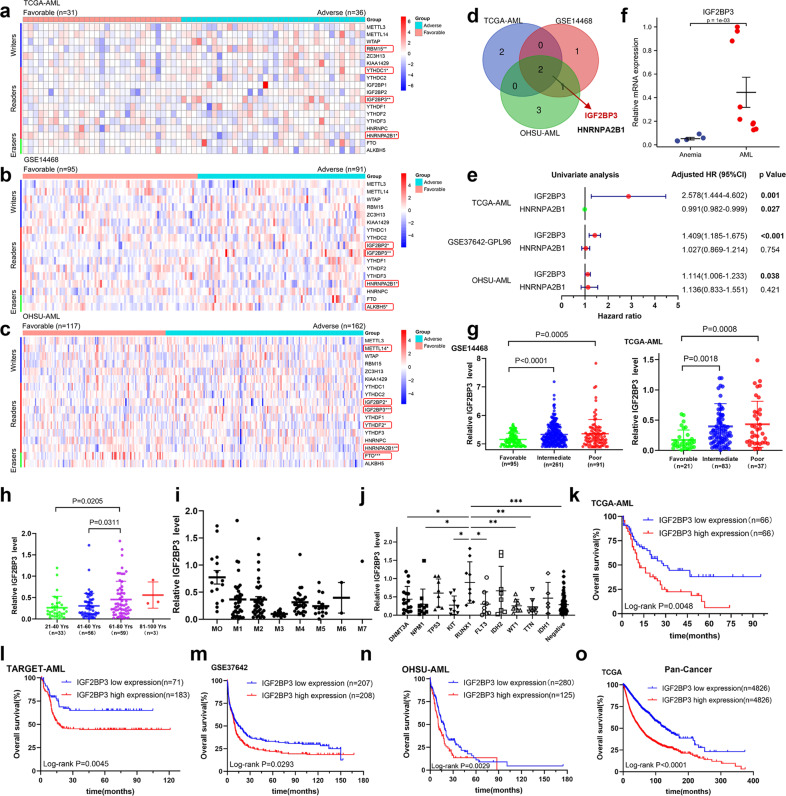
Fig. 1. High-throughput library screening identifies IGF2BP3 as a core m6A regulator in AML.
a–c Heatmap representation of transcriptome array data for the expression levels of m6A-associated regulators in AML from the TCGA-AML, GSE14468, and OHSU-AML datasets. d Both IGF2BP3 and HNRNPA2B1 are significantly differentially regulated m6A functional effectors in different datasets. e A forest plot showing the HR and 95% CI for the association between IGF2BP3 and HNRNPA2B1 candidate genes and overall survival times in patients with AML calculated by univariate Cox regression analysis. f Real-time PCR was used to determine the expression of IGF2BP3 in bone marrow specimens from patients with AML. g The aberrantly high expression of IGF2BP3 in AML patients was significantly correlated with more unfavorable clinical characteristics on measures such as cytogenetic risk stratification. h Expression of IGF2BP3 mRNA with increasing age. i, j IGF2BP3 expression was lowest in patients with the AML-M3 subtype (French-American-British classification) and higher in patients with RUNX1 mutation. k–n Kaplan–Meier survival analysis showed that AML patients with high IGF2BP3 expression exhibited worse overall survival, based on analysis of TCGA, TARGET, GSE37642, and OHSU-AML datasets. o Pancancer analysis of 9652 tumor patients in the TCGA cohort showed that high expression of IGF2BP3 was strongly associated with poor prognosis. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.