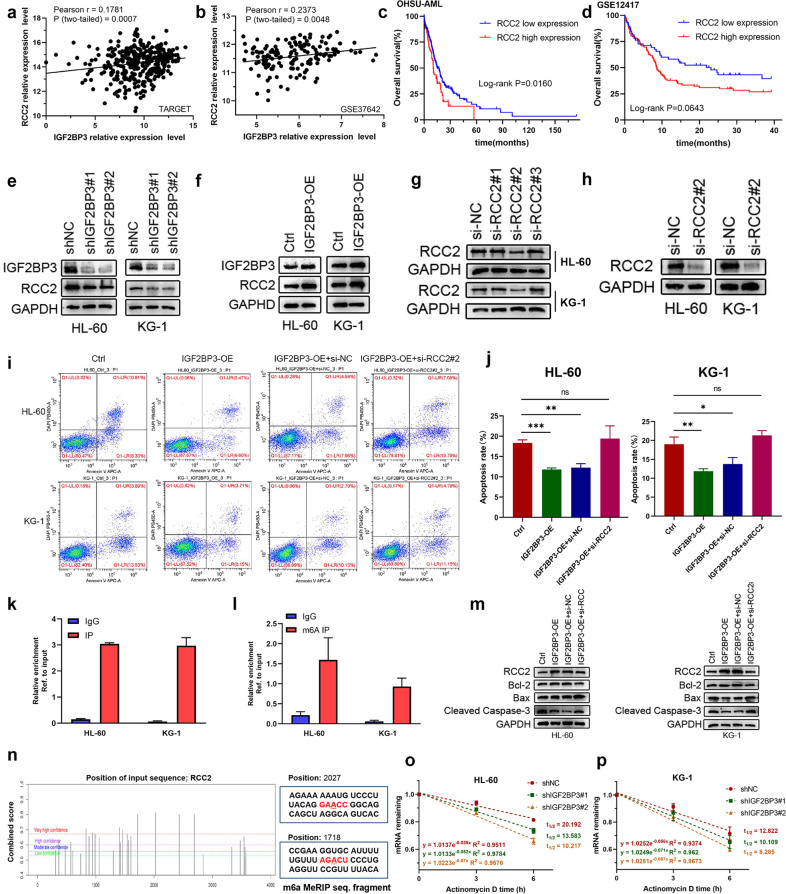
Fig. 6. IGF2BP3 regulates RCC2 expression in an m6A-dependent manner.
a, b RCC2 expression was positively correlated with IGF2BP3 expression in the GSE37642 and TARGET datasets. c, d Kaplan–Meier survival analysis revealed that high RCC2 expression indicated a poor prognosis in AML patients. e, f Protein expression level of RCC2 following knockdown or overexpression of IGF2BP3 in HL-60 and KG-1 cells. g, h The interference efficiency of the siRNAs was evaluated to confirm the feasibility of the siRNAs, and si-RCC2#2 was found to be effective in reducing RCC2 expression. i, j Apoptosis was detected by flow cytometry. RCC2 deficiency promoted the induction of apoptosis by IGF2BP3 overexpression. k The mRNA of RCC2 was enriched by the anti-IGF2BP3 antibody compared to IgG in the HL-60 and KG-1 cell lines. l The mRNA of RCC2 was enriched by the m6A-specific antibody compared to IgG in the HL-60 and KG-1 cell lines. m Overexpression of IGF2BP3 restored the increases in the levels of proapoptotic proteins (Bax and cleaved Caspase 3) caused by silencing RCC2, and the level of the antiapoptotic protein Bcl-2 was slightly decreased. n The potential m6A sites in RCC2 were predicted by SRAMP. The different colored lines indicate different confidence levels. o, p Loss of IGF2BP3 reduced RCC2 stability in HL-60 and KG-1 cells. Transfected cells were treated with 5 µg/ml actinomycin D for 0 h, 3 h, or 6 hours prior to RNA extraction. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.