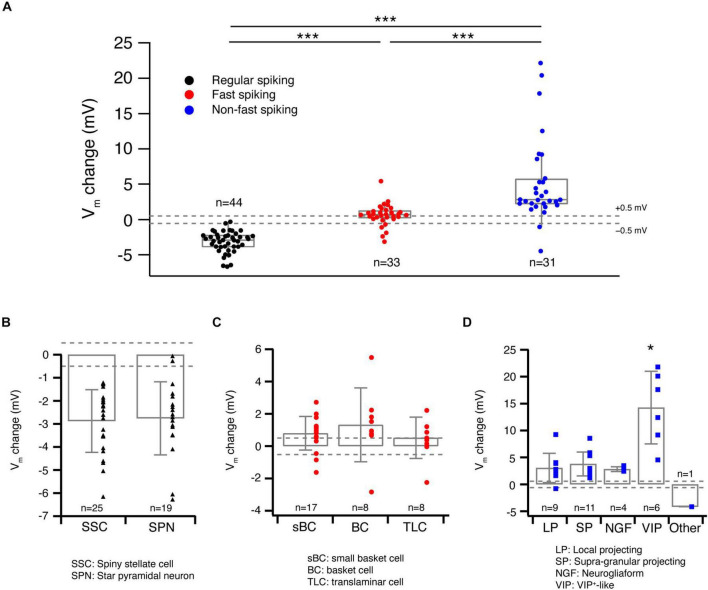
FIGURE 3.
Acetylcholine-induced Vm changes are related to the L4 RS, FS and nFS neuron (sub)types. (A) Box plots of ACh-induced Vm changes in L4 RS, FS and nFS neurons. Individual data points are given on the right. P value was calculated using the non-parametric Wilcoxon–Mann–Whitney two-sample rank test. *** p < 0.001. Dashed lines indicate the Vm change at ±0.5 mV. (B) Histograms of ACh-induced Vm changes for two L4 RS neuron subtypes: spiny stellate cells and star pyramidal neurons. No statistically significant difference was found between two subtypes. (C) Histograms of ACh-induced Vm changes for three L4 FS neuron subtypes: small basket cells, basket cells, and translaminar cells. No statistically significant difference was found among three subtypes. (D) Histograms of ACh-induced Vm changes for five L4 nFS neuron subtypes: local projecting (putative SST+, non-Martinotti cell-like), supragranular projecting (putative SST+, Martinotti cell-like), NGF, VIP+-like and unclassified interneurons. VIP+-like interneurons show the strongest depolarisation of the five subtypes. Statistically significant differences (*) were found between VIP+-like and three other interneuron subtypes (LP, SP, NG).