FIGURE 6.
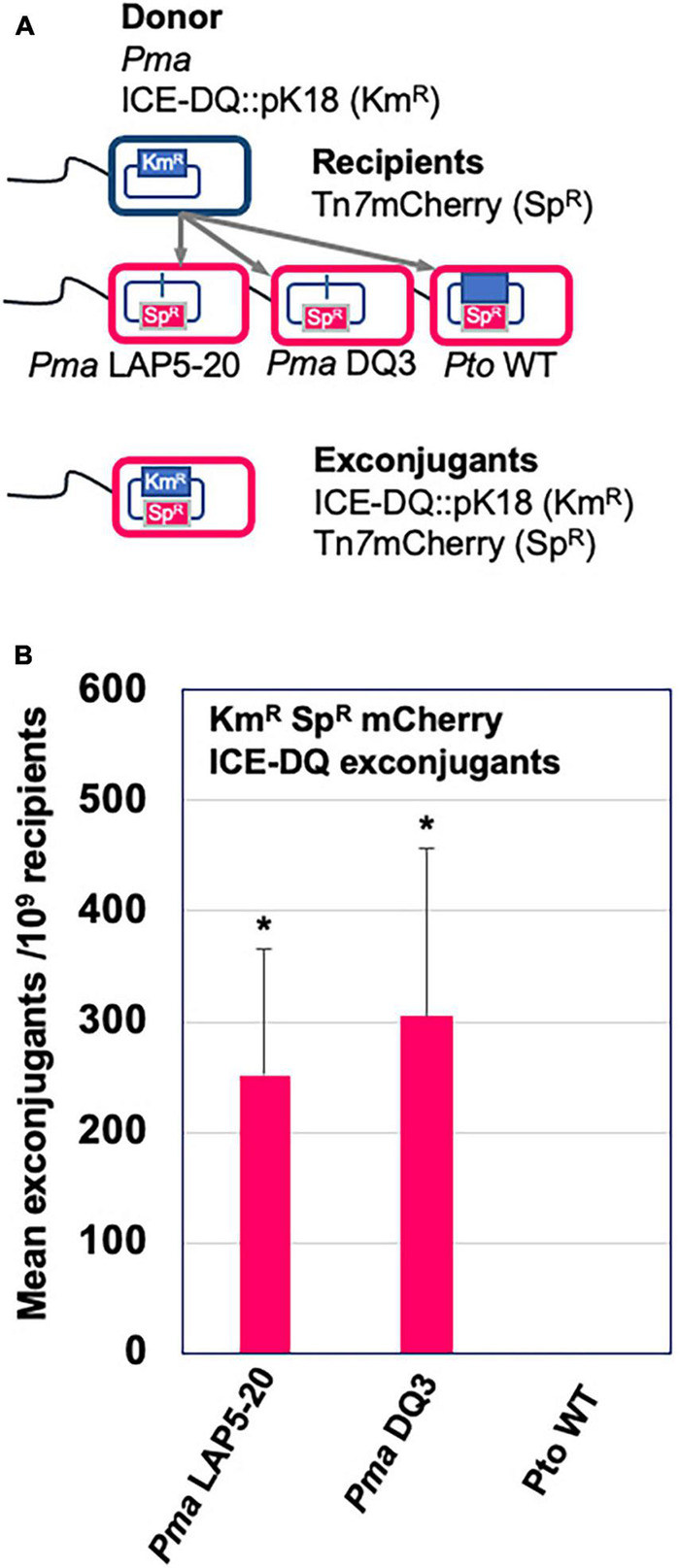
ICE-DQ can be readily transferred into PmaES4326 strains that lack the ICE element. (A) Schematic representation of the conjugation strategy for monitoring ICE-DQ transfer between strains. The ICE-DQ of the donor strain was marked with kanamycin resistance by single crossover integration the pK18ms plasmid (Pma ICE-DQ:pK18). The recipient strains Pma DQ3 (ΔICE-DQ targeted), Pma LAP5-20 (ΔICE-DQ passage-derived) and PtoDC3000 were marked by introduction of a spectinomycin resistance Tn73xmCherry transposon. Donor and recipients were co-cultured on LM media and ICE-DQ:pK18 mCherry expressing ICE-DQ exconjugants were recovered on kanamycin and spectinomycin. (B) ICE-DQ:pK18 exconjugant recovery frequencies/109 recipients were determined based on kanamycin and spectinomycin exconjugants per spectinomycin resistant recipients as determined by dilution plating. Values are means and standard deviations of three biological replicates. *p < 0.05 compared to Pto WT strain as determined by unpaired one-tailed t-test.
