FIGURE 3.
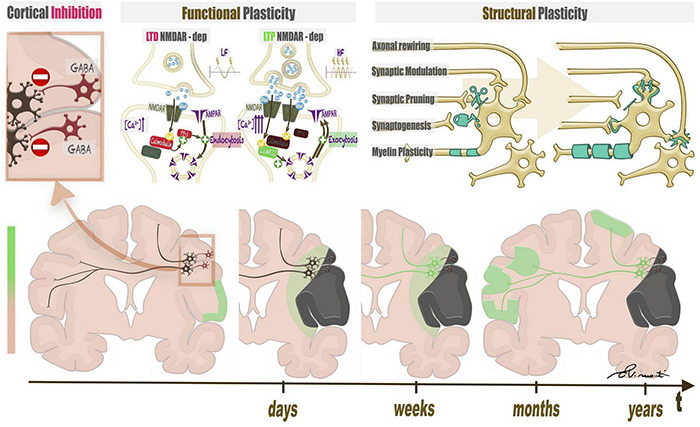
Structural and functional plasticity of language triggered by a focal lesion. The left upper panel represents the baseline condition of the brain, characterized by widespread inhibition mediated by GABA interneurons. When a lesion attacks eloquent brain areas, the damage triggers disinhibition of nearby neural networks, possibly leading to functional and structural plasticity. Functional plasticity (central upper panel) at the synaptic level consists of long term potentiation (LTP) or depotentiation (LTD), which depend on an increase in calcium ions in the post-synaptic neurons of inhibitory and excitatory synapses. Structural plasticity (right upper panel) includes changes in synapses, axons, and myelin coating. The lower panel represents a timeline of plastic changes in the brain. After lesion onset, perilesional and contralateral modifications follow.
