Figure 7.
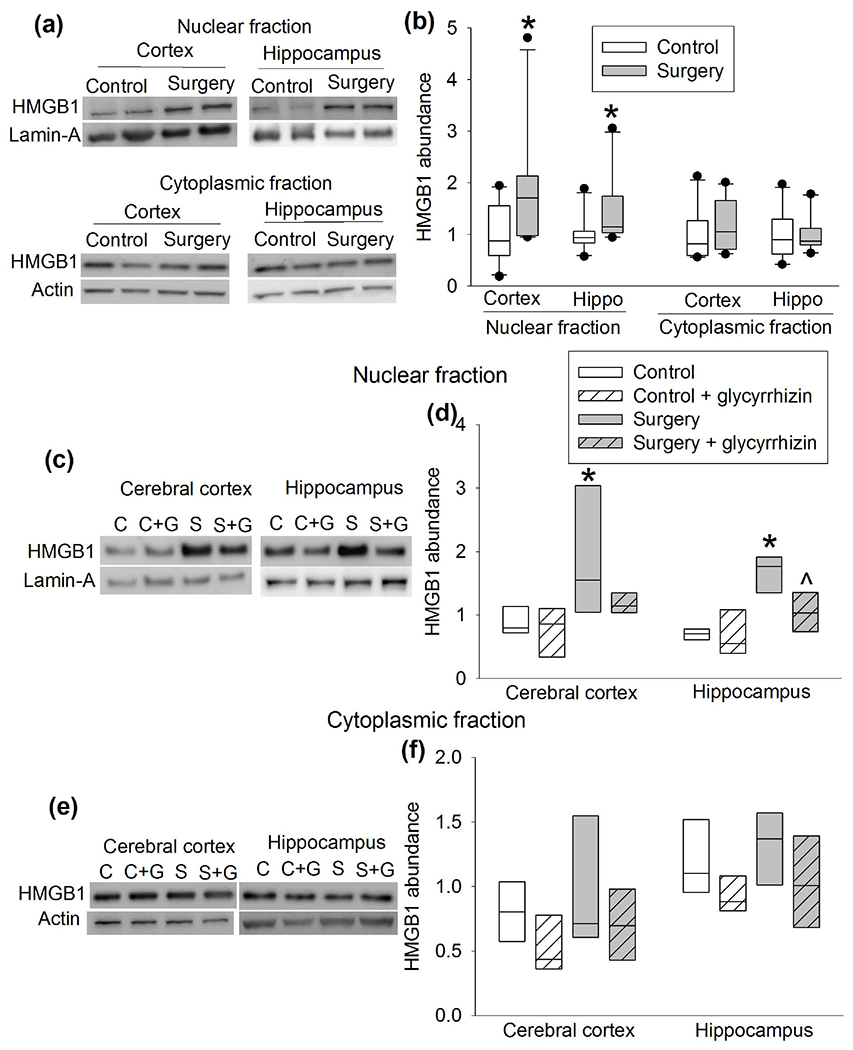
Surgery increased HMGB1 expression. CD-1 mice were subjected to right carotid artery exposure under isoflurane anesthesia. Cerebral cortex and hippocampus were harvested 6 h after the surgery. (a) Representative Western blotting images of samples from mice with or without surgery. (b) Quantitative results of HMGB1 protein abundance in samples from mice with or without surgery. (c) Representative Western blotting images of nuclear proteins from mice with or without surgery in the presence or absence of glycyrrhizin. (d) Quantitative results of HMGB1 protein abundance in nuclear proteins from mice with or without surgery in the presence or absence of glycyrrhizin. (e) Representative Western blotting images of cytoplasmic proteins from mice with or without surgery in the presence or absence of glycyrrhizin. (f) Quantitative results of HMGB1 protein abundance in cytoplasmic proteins from mice with or without surgery in the presence or absence of glycyrrhizin. Results are in box plot format (n = 10 for panel b, = 6 for panels d and f; the n number referred to the number of animals). ● : lowest or highest score (the score will not show up if it falls in the 95th percentile); between lines: 95th percentile of the data; inside boxes: 25th to 75th percentile including the median of the data. * P < 0.05 compared with control. ^ P < 0.05 compared with surgery alone.
