Fig. 4.
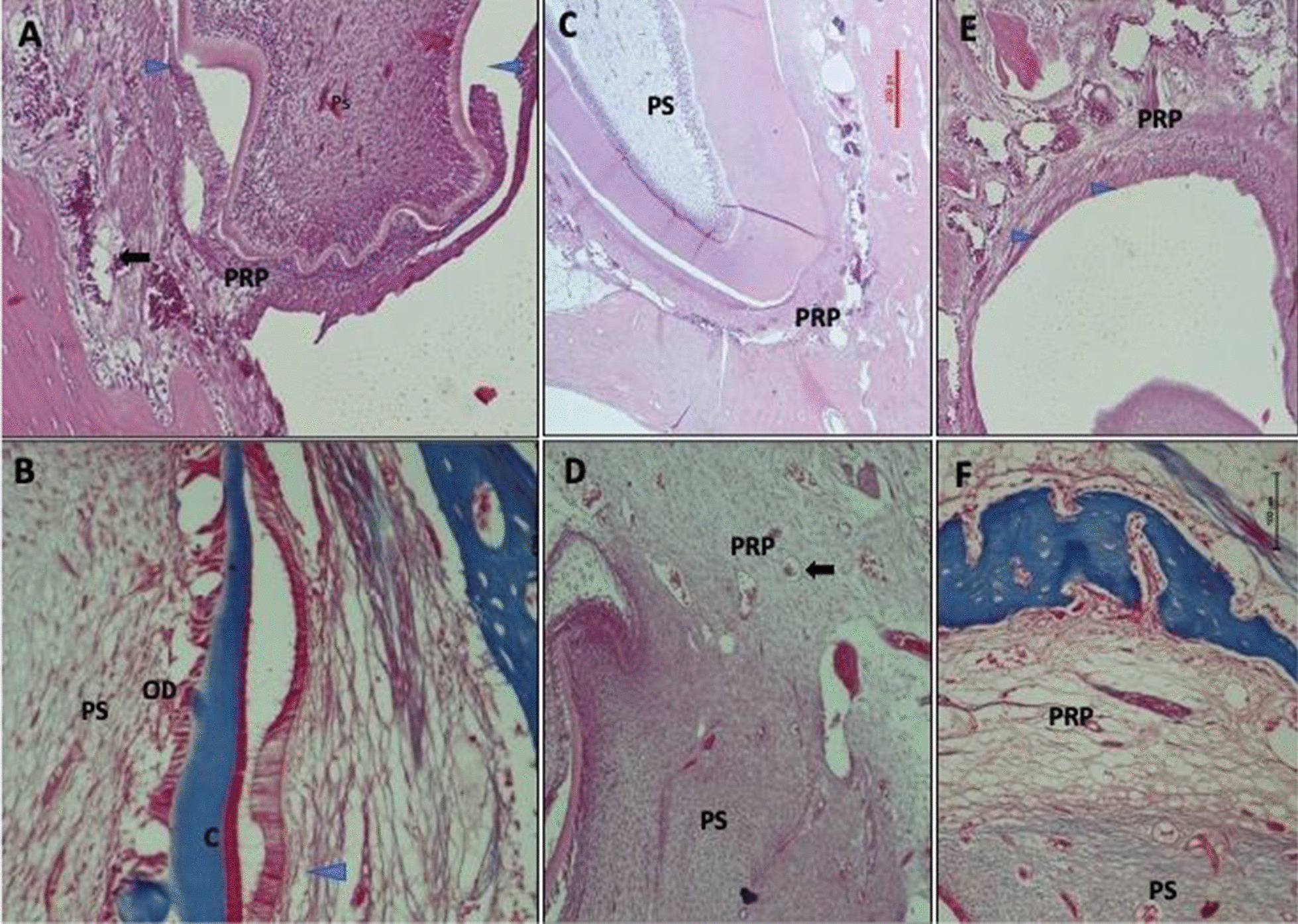
Periapical area after two months of pulp capping with [19] and without (D–F) laser therapy. A Apex continue closing after pulp capping and laser therapy. The periapical area (PRP), fibroblasts with numerous dilated blood vessels (arrow) and mild inflammation. More collagen in periapical and mature PDL next to the area of complete dentine formation and cement formation. Mild inflammation in surrounding bone and bone marrow. B Masson Trichome Image showed the mature PDL and cementum. Odontoblasts palisaded in pulpal side (PS) of dentine. C with complete closure and thick dentine wall the periapical area showed denser collagen fibrous and normal compact viable bone and blood supply. D In teeth without laser therapy, the open apex tooth with neoformed pulpal tissues in the pulp space (PS) do not communicate with the periapical tissues. The clear separation between pulp and periapical tissue is illustrated in Masson trichome stained tissue (E). A closed apex on non-lazed teeth showed mature PDL and the periapical area had scattered inflammatory cells with congested blood vessels. F Mild inflammation and scattered blood vessels were noticed in periapical area (D)
